Table of Contents
Syllogism is an important section in reasoning ability, which tests the candidate’s ability to draw logical conclusions and analyze arguments. Candidates should focus on identifying the relationship between different statements and apply techniques like Venn diagrams or logical reasoning methods to see the connection. This article presents syllogism questions for SBI Clerk exam as these questions are most effective in your exam.
Syllogism Questions for SBI Clerk 2025 Exam
Practicing different types of syllogism patterns and developing the skill to quickly eliminate the wrong options will help candidates answer questions efficiently. By honing these techniques, candidates can gain confidence in solving syllogism questions easily in SBI Clerk Exam 2025.
Recognizing common patterns like ‘all’, ‘some’ or ‘no’ and applying Venn diagrams or logical reasoning helps in solving these questions faster. Below are some of the types of syllogism questions. With consistent practice, candidates can develop the skill to identify valid conclusions and efficiently tackle these questions in the exam.
Directions (1-15): In each of the questions below, few statements are given followed by two conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance from commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follow from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Q1. Statements: Only a few colors are smooth.
All pastel is smooth.
All smooth is Yellow.
Conclusions: I. All the pastel can be colors.
II. Some yellow is not colors.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
Q2. Statements: Only a few engine are hill.
No engine is socket.
Only a few socket is rocket.
Only a few cake is socket.
Conclusions: I. Some engine is not rocket.
II. All rockets can never be engines.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
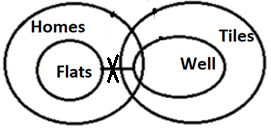
Q3. Statements: All flats are homes.
All well are tiles.
No flat is well.
Only a few homes are well.
Conclusions: I. Some tiles are not flats.
II. A few homes are tiles.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
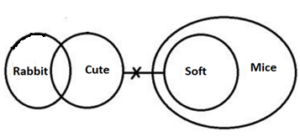
Q4. Statements: Only a few Rabbit is Cute.
No Cute is Soft.
All Soft is Mice.
Conclusions: I. Some Rabbit is not Cute.
II. Some Rabbit is not Soft.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
Q5. Statements: All Copy is Notebook.
Only a few Notebooks are Rough.
All books are Rough.
Conclusions: I. Some Copy being Rough is a possibility.
II. At least some Books are Notebooks.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
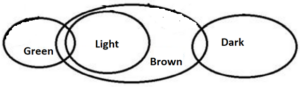
Q6. Statements: Only a few Green is Light.
All Light is Brown.
Only a few Brown is Dark.
Conclusions: I. No Green is Dark.
II. All Brown can be Dark.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
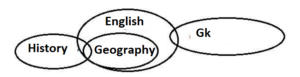
Q7. Statements: Only a few History is Geography.
All Geography is English.
Only a few English are Gk.
Conclusions: I. Some History is Gk.
II. No History is Gk.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
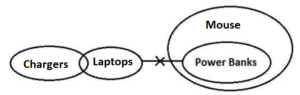
Q8. Statements: Only a few Chargers are Laptops.
No Laptops are Power Banks.
All Power Banks are Mouse.
Conclusions: I. Some Chargers are not Power Banks.
II. Some Mouse are not Laptops.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
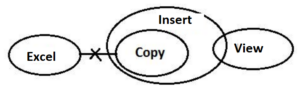
Q9. Statements: No Excel are Copy.
All Copy are Insert.
Only a few Insert are View.
Conclusions: I. Some Copy are View.
II. No Insert are Excel.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
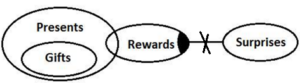
Q10. Statements: All Gifts are Presents.
Only a few Presents are Rewards.
Some Rewards are not Surprises.
Conclusions: I. Some Gifts are not Surprises.
II. Some Presents are not Rewards
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
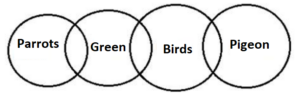
Q11. Statements: Only a few Parrots are Green.
Some Green are Birds.
Only a few Birds are Pigeon.
Conclusions: I. No Green is Pigeon.
II. Some Green are Pigeons.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
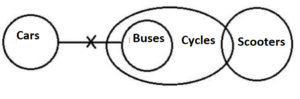
Q12. Statements: No Cars are Buses.
All Buses are Cycles.
Only a few Cycles are Scooters.
Conclusions: I. Some Scooters can be Cars.
II. Some Cycles are not Cars.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
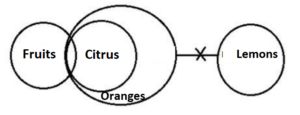
Q13. Statements: Only a few Fruits are Citrus.
All Citrus are Oranges.
No Oranges are Lemons.
Conclusions: I. Some Fruits are not Citrus.
II. Some Fruits are not Lemons.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
Q14. Statements: Some Tiles are not Columns.
All Columns are Rows.
Only a few Rows are Sets.
Conclusions: I. Some Sets are Tiles.
II. All sets are Rows.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
Q15. Statements: Only a few Flowers are Leaves.
All Leaves are Thorns.
No Thorns are Stems.
Conclusions: I. Some Flowers are not Leaves.
II. Some Leaves are not Stems.
(a) If only conclusion I follows
(b) If only conclusion II follows
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow
Directions (16-20): In the question below, some statements are given followed by the conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements disregarding commonly known facts.
Q16. Statements: Only a few Friends are Family.
All Family is Relatives.
No Relatives are Enemies.
Conclusions: I. Some Friends are not Family
II. No Enemies are Family.
(a) Only conclusion I follows.
(b) Only conclusion II follows.
(c) Either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) Both conclusion I and II follow.
Q17. Statements: All Wires are Cables.
Only a few Cables are Pipes.
Only a few Pipes are Strings.
Conclusions: I. Some Wires are Strings.
II. No Wires are Strings.
(a) Only conclusion I follows.
(b) Only conclusion II follows.
(c) Either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) Both conclusion I and II follow.
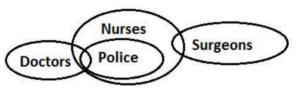
Q18. Statements: Only a few Doctors are Police.
All Police is Nurses.
Only a few Nurses are Surgeons.
Conclusions: I. All Doctors are Nurses.
II. No Surgeons are Police.
(a) Only conclusion I follows.
(b) Only conclusion II follows.
(c) Either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) Both conclusion I and II follow.
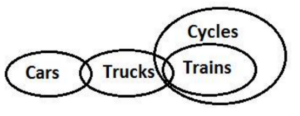
Q19. Statements: Only a few Cars are Trucks.
Only a few Trucks are Trains.
All Trains are Cycles.
Conclusions: I. Some Trucks are not Trains.
II. No Cars are Cycles.
(a) Only conclusion I follows.
(b) Only conclusion II follows.
(c) Either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) Both conclusion I and II follow.
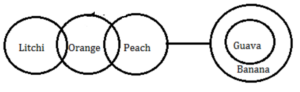
Q20. Statements: Only a few orange is peach.
No peach is banana.
All guavas is bananas.
Some oranges are litchi.
Conclusions: I. All litchi being banana is a possibility.
II. All peach is orange.
(a) Only conclusion I follows.
(b) Only conclusion II follows.
(c) Either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) Neither conclusion I nor II follows
(e) Both conclusion I and II follow.
Solutions
Solutions (1-15):
S1. Ans. (a)
Sol.
S2. Ans. (b)
Sol.
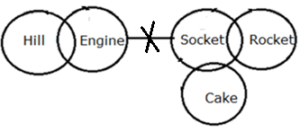
S3. Ans. (e)
Sol.
S4. Ans. (e)
Sol.

S5. Ans. (a)
Sol.
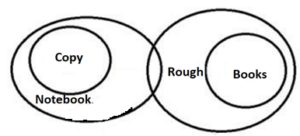
S6. Ans. (d)
Sol.
S7. Ans. (c)
Sol.
S8. Ans. (e)
Sol.
S9. Ans. (d)
Sol.
S10. Ans. (b)
Sol.
S11. Ans. (c)
Sol.
S12. Ans. (e)
Sol.
S13. Ans. (e)
Sol.
S14. Ans. (d)
Sol.
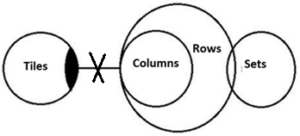
S15. Ans. (e)
Sol.
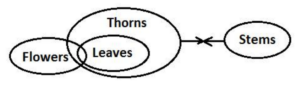
Solutions (16-20):
S16. Ans. (e)
Sol.
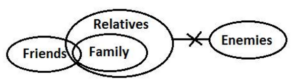
S17. Ans. (c)
Sol.
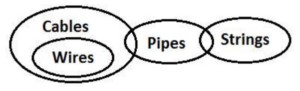
S18. Ans. (d)
Sol.
S19. Ans. (a)
Sol.
S20. Ans. (a)
Sol.
| Related Post | |
| SBI Clerk Exam Date 2025 | SBI Clerk Reasoning Questions |
| SBI Clerk Previous Year Papers | SBI Clerk Cut Off |
| SBI Clerk Salary | SBI Clerk Syllabus |



 Important Blood Relation Questions for S...
Important Blood Relation Questions for S...
 Seating Arrangement Questions for SBI PO...
Seating Arrangement Questions for SBI PO...
 Inequality Questions for Bank Exams
Inequality Questions for Bank Exams




