Table of Contents
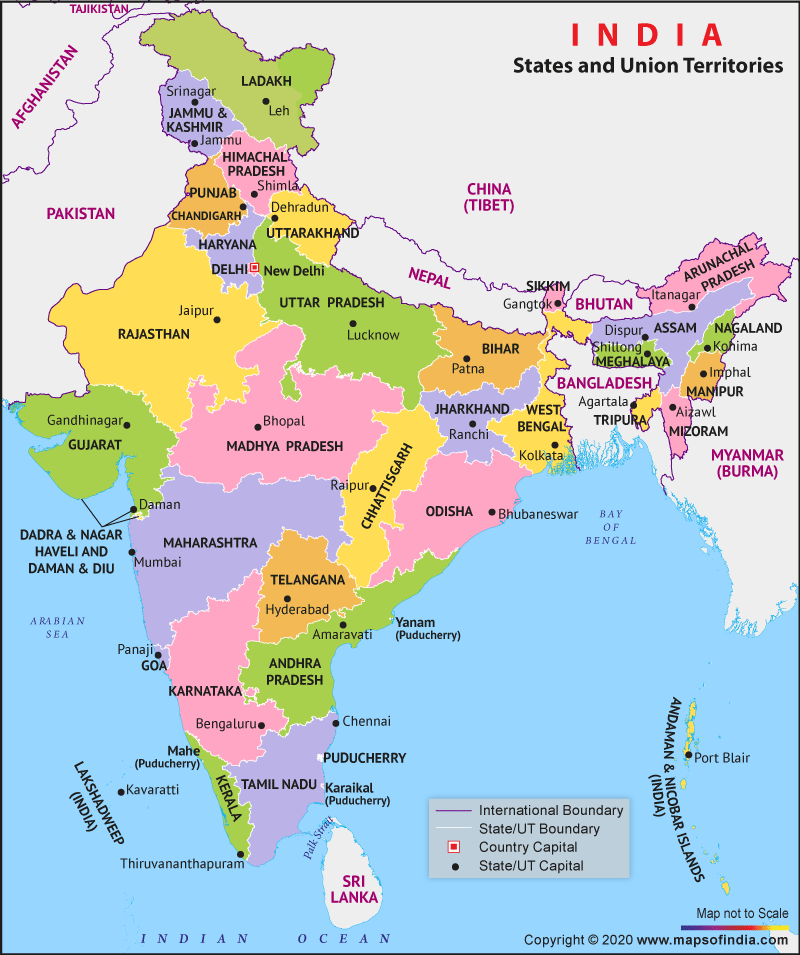
India, the seventh-largest country in the world by land area, is a union of states and union territories, each with its own unique cultural, historical, and geographical identity. Currently, India comprises 28 states and 8 union territories, and each state has its own capital that serves as the administrative, legislative, or judicial hub. Understanding the states and their capitals is not only essential for academic and competitive exam purposes but also helps in gaining a deeper insight into the country’s diverse political and regional landscape.
States and Capitals of India
India is a diverse country divided into 28 states and 8 union territories. Known for its vibrant culture and stunning geographical diversity, each state and union territory has its own unique importance and charm. Every region is steeped in history, with stories that reflect its deep cultural roots. Located in southern Asia, India operates under a parliamentary system of government. To efficiently manage such a vast country, the Indian Constitution provides for the creation of states to ensure smoother governance under the central government.
The states and union territories are further divided into smaller administrative units, such as districts and subdivisions, for better management. In this article, we bring you a detailed list of India’s states and union territories.
List of States and Capitals Of India
India is divided into 28 states and 8 union territories. In 2019, a significant change occurred with the implementation of the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act. This led to the creation of two new union territories, Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh, on 31st October, making this date an important milestone in the country’s history. Keep reading this article for a complete list of the States and Capitals of India, along with details about the Union Territories.
States of India and their Capitals
| S.No | States Name | Capital | Founded on |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Amaravati | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Itanagar | 20 Feb. 1987 |
| 3 | Assam | Dispur | 26 Jan. 1950 |
| 4 | Bihar | Patna | 26 Jan. 1950 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Raipur | 1 Nov. 2000 |
| 6 | Goa | Panaji | 30 May. 1987 |
| 7 | Gujarat | Gandhinagar | 1 May. 1960 |
| 8 | Haryana | Chandigarh | 1 Nov. 1966 |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Shimla (summer) Dharmashala (winter) |
25 Jan. 1971 |
| 10 | Jharkhand | Ranchi | 15 Nov. 2000 |
| 11 | Karnataka | Bengaluru | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| 12 | Kerala | Thiruvananthapuram | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | Bhopal | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| 14 | Maharashtra | Mumbai | 1 May. 1960 |
| 15 | Manipur | Imphal | 21 Jan. 1972 |
| 16 | Meghalaya | Shillong | 21 Jan. 1972 |
| 17 | Mizoram | Aizawl | 20 Feb. 1987 |
| 18 | Nagaland | Kohima | 1 Dec. 1963 |
| 19 | Odisha | Bhubaneswar | 26 Jan. 1950 |
| 20 | Punjab | Chandigarh | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| 21 | Rajasthan | Jaipur | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| 22 | Sikkim | Gangtok | 16 May. 1975 |
| 23 | Tamil Nadu | Chennai | 26 Jan. 1950 |
| 24 | Telangana | Hyderabad | 2 Jun. 2014 |
| 25 | Tripura | Agartala | 21 Jan. 1972 |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | Lucknow | 26 Jan. 1950 |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | Dehradun (Winter) Gairsain (Summer) |
9 Nov. 2000 |
| 28 | West Bengal | Kolkata | 1 Nov. 1956 |
Union Territories of India and their Capitals
Union Territories in India are regions that are governed directly by the federal government of the country. Unlike states, Union Territories have less autonomy and are usually administered by a Lieutenant Governor or Administrator appointed by the President of India. These territories are often created for various administrative and governance purposes. As of now, there are 8 Union Territories in India:
The two union territories, which are Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh, are added to the list of Union Territories of India under the Reorganisation Act passed by the parliament on 5-6 August 2020. The table below shows the detailed lists of the 8 union territories of the country.
| Union Territories Names | Capital | Founded on |
|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Sri Vijaya Puram | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 1 Nov. 1966 |
| Dadra & Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | Daman | 26 Jan. 2020 |
| Delhi | New Delhi | 9 May. 1905 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Srinagar (Summer) Jammu (Winter) |
31 Oct 2019 |
| Ladakh | Leh | 31 Oct 2019 |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti | 1 Nov. 1956 |
| Puducherry | Puducherry | 1 Nov. 1954 |
Delhi, Puducherry, and Jammu & Kashmir do not operate in the same manner as the other five Union Territories of India since they have partial statehood status and have their own elected legislative assemblies
About India
India is mainly located in South Asia and is officially known as the Republic of India. It comprises a total area of 3,287,263 sq. km and has an estimated population of 135.26 crores (2019), which makes it the world’s second-most populous country.
India is a federal constitutional republic and is known as the world’s most populous democracy. It is governed by the parliamentary system. Earlier, there were 28 states and 8 Union Territories, but the Government of India revoked Article 370 in Jammu and Kashmir and declared it a union territory along with Ladakh. After the implementation of the decision, currently, there are 28 states and 8 Union Territories, as Daman & Diu is merged with Dadar and Nagar Haveli.
Each state and union territory has an administrative, legislative, and judicial capital of its own. (The Union territories of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh have a common high court as per the new guidelines)
Types of Capital
Given below is a brief differences between the different kinds of capitals.
- An administrative capital refers to the one where all the offices of the executive government are situated.
- A legislative capital refers to the one where the state assembly convenes.
- A judicial capital refers to the one where the territorial high courts are located.
All the states, along with two union territories, Pondicherry and the National Capital Territory of Delhi, have an elected form of government and legislatures. They are headed by their elected Chief Minister, who is elected for a term of five years. The Central government directly rules all the other union territories and has a representative in each UT known as the governor. Under the States Reorganisation Act of 1956, the states were reorganised based on the language that is used there.
Capital of India
New Delhi is the capital of India. The foundation stone of New Delhi was laid by Emperor George V during the Delhi Durbar of 1911. British architects Sir Edwin Lutyens and Sir Herbert Baker designed it. Finally, Viceroy and Governor-General of India Lord Irwin inaugurated it on 13 February 1931.
Financial Capital of India
Mumbai is known as the financial, commercial, and entertainment capital of India because it accounts for 25% of industrial output, 5% of India’s GDP, and also 70% of the capital transactions in the Indian economy and has financial institutions of national importance such as the Reserve Bank of India, the Bombay Stock Exchange Market, and the corporate headquarters of many Indian companies.
As per an article in The Times of India, Mumbai has ceded its position as the financial capital of India based on data released by Oxford Economics, and the centre is shifting to Gurugram and Delhi.
Difference Between States and Union Territories
The table below highlights detailed information about the difference between the states and Union Territories of India.
| State | Union Territory |
| A state is the division of a nation that has its own legislative assembly. | A Union Territory doesn’t have a legislative assembly ( Delhi, Puducherry, and Jammu & Kashmir) |
| Chief Minister is the real head. | The lieutenant is the real head. |
| The executive head is the Governor. | The executive head is the President. |
| Administered by the Chief Minister. | Administered by the Administrator, appointed by the President. |
| States have Autonomous Power. | UTs do not have it. |
States and Capitals of India: Articles in the Constitution
Under Part 1 of the Constitution, Articles 1 to 4 describe India and its territories.
- Article 1 describes India as the “Union of States” and not “Federation of States” The names of states and their territories are mentioned in the first schedule of the Constitution.
- Article 2 allows the parliament to ‘admit into the Union of India or establish new states on such terms as it thinks or finds fit.’ Hence, it gives power to parliament to establish new states.
- Article 3 permits the parliament to
a) form a new state by the separation of the existing territory
b) increase the area of the state as seems fit
c) diminish the area of any state as seems fit
d) alter the boundary of any state as seems fit
e) alter the name of any state as seems fit
Specialities Of Different Indian States
India is a land of diversity, where each state holds its own unique charm and attractions. From the bustling metropolises of Maharashtra to the serene backwaters of Kerala, every state showcases a distinctive cultural, historical, and geographical identity. Here in this table, we have tried to cover in a minute way the rich diversity of our country.
| Specialities Of Different Indian States | |
|---|---|
| Indian States | Specialization |
| Andhra Pradesh | Spicy cuisine, historical sites, rich culture |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Breathtaking landscapes, diverse tribal cultures, Tawang Monastery |
| Assam | Tea plantations, Kaziranga National Park, Bihu dance, silk weaving |
| Bihar | Historical significance, Buddhist pilgrimage sites, Madhubani art |
| Chhattisgarh | Tribal heritage, mineral resources, and Chitrakote Waterfall |
| Delhi | Iconic landmarks, India Gate, and cultural diversity |
| Goa | Beautiful beaches, nightlife, Indian-Portuguese blend, seafood cuisine |
| Gujarat | Industrial strength, Rann of Kutch, festivals, Sabarmati Ashram |
| Haryana | Agricultural productivity, industries, Chandigarh |
| Himachal Pradesh | Hill stations, adventure tourism, Dalai Lama’s residence |
| Jharkhand | Mineral resources, tribal culture, and Betla National Park |
| Karnataka | IT industry, historical sites, Bharatanatyam dance |
| Kerala | Backwaters, Ayurveda, greenery, high literacy rate |
| Maharashtra | Financial hub, Bollywood, Gateway of India, Vada Pav |
| Manipur | Traditional dance, Loktak Lake, vibrant festivals |
List of the Indian States and their Languages
In India, every state has its own language, and our country is also well known because of its culture, languages and religion. The table below shows the language of each state.
| Sl.No. | States | Language |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Telugu and Urdu |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Miji, Apotanji, Merdukpen, Tagin |
| 3 | Assam | Assamese |
| 4 | Bihar | Hindi |
| 5 | Chattisgarh | Hindi |
| 6 | Goa | Marathi and Konkani |
| 7 | Gujarat | Gujarati |
| 8 | Haryana | Hindi |
| 9 | Himachal Pradesh | Hindi and Pahari |
| 10 | Mizoram | Mizo and English |
| 11 | Jammu & Kashmir | Kashmiri, Dogiri, Urdu, Ladakki, Pahari, Panjabi and Dadri |
| 12 | Jharkhand | Hindi |
| 13 | Karnataka | Kannada |
| 14 | Kerala | Malayalam |
| 15 | Madhya Pradesh | Hindi |
| 16 | Maharashtra | Marathi |
| 17 | Manipur | Manipuri |
| 18 | Meghalaya | Khashi, Jaintia and Garo |
| 19 | Nagaland | Ao, Konyak, Angami, Sema and Lotha |
| 20 | Odisha | Oriya |
| 21 | Punjab | Punjabi |
| 22 | Rajasthan | Rajasthani and Hindi |
| 23 | Sikkim | Bhutia, Hindi, Nepali, Lepcha, Limbu |
| 24 | Tamil Nadu | Tamil |
| 25 | Tripura | Bengali, Tripuri, Manipuri, Kakborak |
| 26 | Telangana | Telugu |
| 27 | Uttar Pradesh | Hindi |
| 28 | Uttrakhand | Hindi |
| 29 | West Bengal | Bengali |
Delhi, Puducherry, J & K are different from other Union Territories
- In India, the majority of the states and three union territories, i.e. Puducherry, Delhi, and Jammu and Kashmir, possess elected legislature and government.
- Currently, there are a total of eight union territories in India, out of which 3, i.e. Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi, and Puducherry, have their elected members and the Chief Minister, and these are granted with partial statehood by an amendment to the Constitution.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi, and Puducherry are the only union territories that possess their own legislative assembly and executive council and operate like states. The remaining union territories are controlled and regulated by the Union of the country, which is why named as union territories.



 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 World Malaria Day 2025
World Malaria Day 2025




