Table of Contents
The SBI Clerk exam is a key entry-level position in the banking and finance sector, representing an important starting point in a career with the State Bank of India. One of the most important topics in this exam is Quantitative Aptitude, which is a significant part of the paper. Out of a total of 100 questions, 35 are devoted to Quantitative Aptitude. In this article, we will share a collection of 2024 SBI Clerk Quantitative Aptitude Questions 2024 to help you prepare.
Here, we present the main topics of Quantitative Aptitude, which is an important section of the SBI Clerk 2024 exam. Understanding these topics not only enhances problem-solving skills but also increases accuracy and confidence, making it an important part of your preparation journey.
- Simplification
- Approximation
- Missing Series
- Quadratic Equation
- Data Interpretation (Bar, Line, Pie, Tabular)
- Data Sufficiency
- Wrong Series
- Time & Work, Pipes & Cisterns
- Problems on Ages
- Average, Ratio, Percentage, Profit & Loss
- Simple Interest & Compound Interest
- Speed, Distance & Time
- Permutation & Combination
- Boat & Stream
- Mensuration
- Volumes
- Probability
- Partnership
- Mixture & Allegation
SBI Clerk Quantitative Aptitude Questions 2024
Directions (1 – 10): What should come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions?
Q1. (7294 – 3241 + 716) – (3267 + 2425 – 961) = ?
(a) 35
(b) 48
(c) 43
(d) 38
(e) 47
Q2. 1217 + 841 – 724 + 819 = ? + 1843
(a) 210
(b) 310
(c) 360
(d) 270
(e) 410
Q3. 0.06 × 0.84 = ? × 1.2 × 0.015
(a) 8.2
(b) 6.4
(c) 2.6
(d) 3.8
(e) 2.8
Q4. 8.41 + 6.25 + 0.79 = ? – 0.55
(a) 17
(b) 14.9
(c) 13.9
(d) 16
(e) 14.7
Q5. 616 + 472 – 811 + 317 = ? + 576
(a) 28
(b) 16
(c) 24
(d) 18
(e) 14
Q6. Average of present age of A and C is 29 years and C is 8 years younger than B. Ratio of present age of A to present age of B is 6:5. Find present age of B?
(a) 32 years
(b) 36 years
(c) 28 years
(d) 30 years
(e) 16 years
Q7. A boat can travel with the speed of 17 kmph in upstream. If the speed of river is 3 kmph, then find the speed of boat in downstream in the same river.
(a) 23 kmph
(b) 20 kmph
(c) 25 kmph
(d) 19 kmph
(e) 21 kmph
Q8. If a shopkeeper marks an article 20% above cost price and sold it at 5% discount and get Rs. 28 profit. Find difference between C.P. and market price of article?
(a) Rs. 50
(b) Rs. 45
(c) Rs. 32
(d) Rs. 40
(e) Rs. 44
Q9. The ratio of speed of two trains which are running in the same direction is 4 : 5. The train having higher speed crosses the second train in 30 seconds and a pole in 4 seconds respectively. Find the ratio of their lengths.
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 2 : 3
(c) 3 : 5
(d) 4 : 5
(e) 6 : 7
Q10. A train crosses a man, who is running in the same direction of train at the speed of 2m/sec. in 10 seconds. The same train crosses a tunnel in 54 seconds. If speed of train is 72 km/h then what is the length of tunnel?
(a) 850 m
(b) 800 m
(c) 900 m
(d) 750 m
(e) 650 m
Q11. 4, 7, 13, 24, 42, 69, ?
(a) 91
(b) 107
(c) 112
(d) 98
(e) 102
Q12. 7, 13, 19, 29, 37, 43, ?
(a) 61
(b) 57
(c) 53
(d) 51
(e) 55
Q13. ?, 5, 11, 23, 43, 73, 115
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
(e) 5
Q14. 32, ?, 24, 60, 210, 945, 5197.5
(a) 12
(b) 8
(c) 15
(d) 18
(e) 16
Q15. 5, 3, 3, 5, 15, 69, ?
(a) 319
(b) 287
(c) 361
(d) 407
(e) 443
Directions (21–25): The following table shows the total no. senior citizen of different age group in Japan. Table also shows the ratio of male to female in them. Study the table carefully to answer the following questions.
| Age group (in year) | Total no. of senior citizen | Ratio of male to female |
| 50–60 | 2400 | 5 : 3 |
| 61–70 | 3200 | 3 : 1 |
| 71–80 | 4800 | 7 : 5 |
| 81–90 | 6000 | 2 : 1 |
Q21. Total no. of female senior citizens of age group (50–60) years are how much percent more or less than female senior citizens of age group (61–70) years?
(a) 12.5% more
(b) 12.5% less
(c) 10.5% more
(d) 10.5% less
(e) 8.5% more
Q22. What is the average no. of male senior citizens of age group (61–70) years and (81–90) years?
(a) 3600
(b) 2600
(c) 3200
(d) 2800
(e) 2300
Q23. If senior citizens of age group (81 –90) were died due to bad health then senior citizen now of this age group are what percent of total senior citizens of age group (61–70) years and (71–80) years together?
(a) 50%
(b) 60%
(c) 54%
(d) 64%
(e) 45%
Q24. If 20% male senior citizens of age group (71 –80) yrs are pensioners then how many male senior citizens are non–pensioner of the same age group?
(a) 2140
(b) 2440
(c) 2240
(d) 2420
(e) 2040
Q25. What is the difference between total male and total female senior citizen of age group (50 –60) and (61 –70) yrs together?
(a) 2300
(b) 2100
(c) 2400
(d) 2200
(e) 1850
Direction (26-30): Given below the table shows total number of room booked in five different hotels on five days of a week. Read the table carefully and answer the questions:
| Hotels | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday |
| Oberai | 360 | 280 | 560 | 520 | 480 |
| Lodhi | 260 | 275 | 225 | 215 | 305 |
| Taj | 640 | 480 | 290 | 375 | 275 |
| Grand | 280 | 250 | 300 | 720 | 220 |
| Eros | 155 | 145 | 265 | 275 | 315 |
Q26. Total rooms booked in ‘Oberai’ on Tuesday & Thursday together is what percent less than total rooms booked in ‘Grand’ on Monday & Thursday?
(a)25%
(b)20%
(c)16%
(d)34%
(e)48%
Q27. Find difference between total number of rooms booked in ‘Oberai’, ‘Lodhi’ & ‘Taj’ on Monday together and total number of rooms booked in ‘Taj’ , ‘Grand’& ‘Eros’ on Thursday together?
(a)140
(b)210
(c)70
(d)110
(e)135
Q28. Find ratio between total rooms booked in ‘Eros’ on Wednesday & Thursday together to total rooms booked in ‘Lodhi’ on Thursday & Friday together?
(a)27: 26
(b)19: 17
(c)29: 32
(d)53 :49
(e)24: 23
Q29. Find sum of average numbers of room booked in ‘Eros’ on Monday, Wednesday & Friday and average number of rooms booked in ‘Grand’ on Monday & Friday?
(a)580
(b)380
(c)495
(d)460
(e)535
Q30. Find percentage increase in rooms booked on Friday in ‘Oberai’ over total rooms booked on Monday in same Hotel?
(a)46%
(b)66
(c)37
(d)28%
(e)33
Directions (31-35): What approximate value will come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions (You are not expected to calculate the exact value).
Q31. 14.98×24.88% of 140.02=?×15
(a) 45
(b) 25
(c) 50
(d) 35
(e) 65
Q32. 1569.99+2190.012-4/9 of 198.12=?/4
(a) 12122
(b) 14478
(c) 18750
(d) 10980
(e) 14688
Q33. 80.04% of 560.05+〖19.02〗^2-∛4913.21=?
(a) 702
(b) 868
(c) 912
(d) 792
(e) 446
Q34. 44.04 ÷ 3.97 × 8.99 ÷ 2.94 + 3.01 = √(?)
(a) 6
(b) 36
(c) 24
(d) 1296
(e) 216
Q35. √(39.94% of 375.08+75.07% of 59.92)=?
(a) 12
(b) 14
(c) 16
(d) 18
(e) 22
Direction (36-40): What approximate value should come in the place of question (?) mark in following questions:
Q36. 56.08% of 549.98 + 251.98 = ?2 – √256.03
(a) 28
(b) 26
(c) 22
(d) 24
(e) 20
Q37. (112.03% of 699.99)/(?×6.99) + 6.993 = 175.03 ×√4.09
(a) 16
(b) 8
(c) 24
(d) 4
(e) 32
Q38. √(3&64.01) + 15.03 % of 1279.99 = ?2
(a) 16
(b) 8
(c) 10
(d) 12
(e) 14
Q39. (240.01+24.99% of 719.99+280.03)/(69.87) = √(3&?)
(a) 64
(b) 8
(c) 1728
(d) 1000
(e) 343
Q40. 32.01 ÷ 1.992 × 127.99 = 2?
(a) 11
(b) 9
(c) 8
(d) 10
(e) 12
Direction (46-50): Pie chart shows percentage of food packet distributed in five different villages & table shows ratio of food packets received to food packets not received by each village. Read the following data carefully and answer the following question.
Note: (i) Number of food packets distributed in D is given in absolute value and other distributed in percentage.
(ii) Total food packets distributed in each village = Food packets received + Food packets not received by village
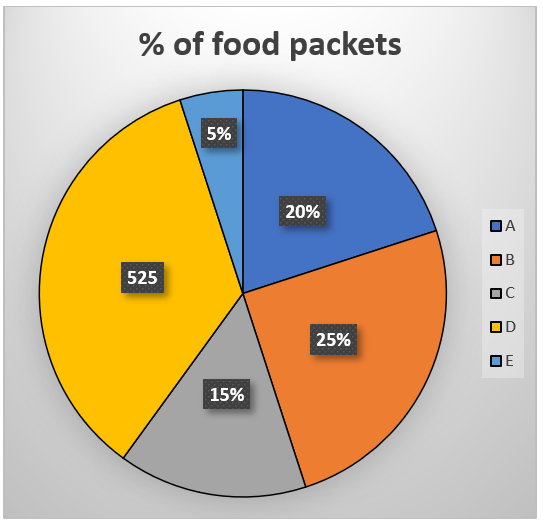
| Villages | Ratio of food packets received to food packets not received by village |
| A | 4 : 1 |
| B | 2 : 1 |
| C | 8 : 1 |
| D | 3 : 2 |
| E | 2 : 1 |
Q46. Find the total number of food packets not received by the villages B & D together?
(a) 335
(b) 325
(c) 375
(d) 275
(e) 225
Q47. Total food packets received by B is what percent less than total food packets distributed for all five village together?
(a) 75%
(b) 62 1/2%
(c) 90 1/3%
(d) 87 1/2%
(e) 83 1/3%
Q48. Total food packets distributed for village B is what percent of food packets distributed for village E?
(a) 600%
(b) 450%
(c) 550%
(d) 400%
(e) 500%
Q49. Find the average number of food packets not received by A, B and C?
(a) 120
(b) 100
(c) 90
(d) 70
(e) 80
Q50. Find the respective ratio of food packets not received by villages A, B & E together to total food packets received by villages C & E together?
(a) 21:26
(b) 21:25
(c) 21: 23
(d) 25 : 21
(e) 21 : 28
Solutions
S1. Ans.(d)
Sol.
4769–4731=?
? = 38
S2. Ans.(b)
Sol. ? = 1217 + 841 + 819 – 724 – 1843
= 2877 – 2567
? = 310
S3. Ans.(e)
Sol.
? = 2.8
S4. Ans.(d)
Sol.
?= 15.45 + 0.55
? = 16
S5. Ans.(d)
Sol.
? = 1405 – 811 – 576
? = 18
S6. Ans.(d)
Sol.
Total age of A and C together = 58 years
Let present age of A and B be 6x and 5x years respectively
Therefore, present age of C = 5x-8
ATQ,
5x-8 + 6x = 58
x= 6
present age of B = 5 ×6 = 30 years
S7. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Speed of boat in upstream = 17 kmph
Speed of river water = 3 kmph
So speed of boat in still water = 17 + 3 = 20 kmph
So speed of boat in downstream = 20 + 3 = 23 kmph
S8. Ans(d)
Sol. let C.P. of article = Rs.100x
Then, M.R.P. of article = x
S.P. of article =
ATQ
x = 2
So, required difference = Rs.40
S9. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Let length of slower train = ℓ 1
Length of faster train = ℓ 2
4x = speed of slower train
5x = speed of faster train
…(i)
And, ℓ 2 = 5x × 4
= 20 x
= 10x
S10. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Speed of man = 2 m/sec
Speed of train = = 20 m/sec
∴ Length of train = (20 – 2) × 10 = 180 m
∴ Length of tunnel = 54 × 20 – 180 = 900 m
S11. Ans. (b)
Sol.
The pattern of the series is –
4+(12+2)=7
7+(22+2)=13
13+(32+2)=24
24+(42+2)=42
42+(52+2)=69
69+(62+2)=107
S12. Ans. (c)
Sol.
The series is set of alternate prime numbers.
7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53
S13. Ans. (c)
Sol.
The pattern of the series is –
3+(1×2)=5
5+(2×3)=11
11+(3×4)=23
23+(4×5)=43
43+(5×6)=73
73+(6×7)=115
S14. Ans. (e)
Sol.
The pattern of the series is –
32×0.5=16
16×1.5=24
24×2.5=60
60×3.5=210
210×4.5=945
945×5.5=5197.5
S15. Ans. (d)
Sol.
The pattern of the series is –
5×1-2=3
3×2-3=3
3×3-4=5
5×4-5=15
15×5-6=69
69×6-7=407
S16. Ans.(d)
Sol.
I. 2x² – 17x+ 36 = 0
2x² – 8x – 9x + 36 = 0
2x (x – 4) – 9 (x – 4) = 0
(2x – 9) (x- 4) = 0
x=9/2, 4
II. 2y² – 19y + 45 = 0
2y² – 10y – 9y + 45 = 0
2y (y- 5) – 9 (y- 5) = 0
(2y- 9) (y- 5) = 0
y=9/2,5
∴ y ≥ x
S17. Ans.(e)
Sol.
I. x² – 25x + 154 = 0
x² – 14x – 11x + 154 = 0
x (x – 14) – 11 (x- 14) = 0
(x – 11) (x- 14) = 0
x = 11, 14
II. y² – 28y + 195 = 0
y² – 13y – 15y + 195 = 0
y (y- 13) – 15 (y -13) =0
(y- 13) (y – 15) = 0
y = 13, 15
∴ no relation
S18. Ans.(a)
Sol.
I. 10/x-24/x² =1
Multiplying by x² on both side
10x – 24 = x²
x² – 10x + 24 = 0
x² – 6x -4x+ 24 = 0
x(x – 6) – 4 (x- 6) = 0
(x – 4) (x- 6) = 0
x= 4, 6
II. 5/y-6/y² =1
Multiplying by y² on both side
5y – 6 = y²
y² – 5y + 6 = 0
y² – 3y – 2y + 6 = 0
y (y- 3) – 2 (y- 3) = 0
(y – 2) (y- 3) = 0
y = 2, 3
∴ x > y
S19. Ans.(d)
Sol.
I. 3x² – 10x – 8 = 0
3x² – 12x + 2x – 8 = 0
3x (x – 4) + 2 (x- 4) = 0
(3x+ 2) (x- 4) = 0
x= -2/3,4
II. 2y²-23y+60=0
2y² – 8y- 15y + 60 = 0
2y (y- 4) -15(y-4) = 0
(y- 4) (2y- 15) = 0
y=4,15/2
∴ y ≥ x
S20. Ans.(a)
Sol.
I. 12x – 16y +16 = 0
3x – 4y + 4 = 0 …(i)
II. 17y- 13x = 12 …(ii)
By multiplying equation (i) by 13 & equation (ii) by 3
39x – 52y = -52
-39x + 51y = 36
y = 16 & x = 20
∴ x > y
S21. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Female Senior citizen of age group (50 – 60) yrs
=3/8×2400=900
Female senior citizen of age group (61 – 70) yrs
=1/4×3200
= 800
Required percentage =(900-800)/800×100
= 12.5% more
S22. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Required average =1/2×(3/4×3200+2/3×6000)
=1/2×6400
= 3200
S23. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Remaining senior citizens
=(100-100/3)% of 6000
= 4000
∴ Required percentage =4000/(3200+4800)×100
=1/2×100
= 50%
S24. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Non–pensioner males =(100-20)% of 7/12 of 4800
=80/100×7/12×4800
= 2240
S25. Ans.(d)
Sol.
Required difference =(5/8×2400+3/4×3200)-(3/8×2400+1/4×3200)
= 1500 + 2400 – 900 – 800
= 2200
S26. Ans.(b)
Sol.
Total rooms booked in Oberai on Tuesday and Thursday = 280 + 520 = 800
Total rooms books in Grand on Monday and Thursday = 280 + 720 = 1000
Required percentage = (1000–800)/1000×100 = 20%
S27. Ans.(d)
Sol.
Total rooms booked in Oberai, Lodhi and Taj on Monday
= 360 + 260 + 640 = 1260
Total rooms booked in Taj, Grand and Eros on Thursday
= 375 + 720 + 275 = 1370
Required difference = 1370 – 1260 = 110
S28. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Total room booked in Eros on Wednesday and Thursday = 265 + 275 = 540
Total rooms booked in Lodhi on Thursday and Friday = 215 + 305 = 520
Required ratio = 540 : 520
= 27 : 26
S29. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Average of room booked in Eros on Monday, Wednesday and Friday
= (155+265+315)/3
= 245
Average of room booked in ‘Grand’ on Monday & Friday
= (280+220)/2
= 250
Required sum = 245 + 250 = 495
S30. Ans.(e)
Sol.
Required percent = (480 –360)/360×100 = 33 1/3%
Solution
S31. Ans.(d)
Sol.
15×25/100×140=? ×15
525/15=?
35=?
S32. Ans.(e)
Sol.
1570+2190-4/9 of 198=?/4
3760-88=?/4
14688=?
S33. Ans.(d)
Sol.
80/100×560+361- ∛4913
448+361-17=?
792=?
S34. Ans.(d)
Sol.
44/4×9/3+3= √(?)
√(?) =11×3+3
36 = √(?)
? =1296
S35. Ans.(b)
Sol.
√(40%×375+75%×60) = ?
? = √(150+45)
? = √195
? = 14
S36. Ans(d)
Sol. 56/100×550+252= ?2 – √256
308 + 252 + 16 = ?2
576 = ?2
? = 24
S37. Ans(a)
Sol. (112/100×700)/(?×7) + 343 = 175 ×2
784/(?×7) = 350 – 343
784/(?×7) = 7
? = 784/49
? = 16
S38. Ans(e)
Sol. 4 + 15/100 ×1280= ?2
4 + 192 = ?2
? = 14
S39. Ans(d)
Sol. (240+25/100×720+280)/70= √(3&?)
(240+180+280)/70 =√(3&?)
700/70=√(3&?)
10 = √(3&?)
? = 1000
S40. Ans(d)
Sol. 25 ÷ 22 × 27 = 2?
2(5-2) ×27 = 2
210 = 2?
? = 10
S41. Ans (b)
Sol. (A+B+C)=(2×(29000+37000+34000))/2
A+B+C=100000
So, require income =100000-(2×34000)
=100000-68000=Rs 32000
S42. Ans.(d)
Sol.
Total age of A and C together = 58 years
Let present age of A and B be 6x and 5x years respectively
Therefore, present age of C = 5x-8
ATQ,
5x-8 + 6x = 58
x= 6
present age of B = 5 ×6 = 30 years
S43. Ans. (c)
Sol. Number of boys in the class = 72×5/9
= 40
Number of girls in the class = 72×4/9
= 32
Required average = ((60×72)-(40×80))/32
= (4320-3200)/32
= 35 kg
S44. Ans (c)
Sol. Total score of Rohit sharma in 11 matches =11×85=935
Total score in first four matches =4×72=288
Total score in next six matches =6×90=540
So, required runs =935-288-540=107
S45. Ans (d)
Sol. let present age of Deepak, Sanjay and Harish be x, y and z years respectively.
ATQ,
⟹ (x-4)/(y-4)=3/4
4x-3y=4 …….(i)
⟹ x+y+z=26×3=78 …..(ii)
⟹ z=y-11 …..(iii)
From (i), (ii) and (iii)
x=25,y=32,z=21
So, present age of Sanjay =y=32 years
S46. Ans. (a)
Sol.
Total number of food packets not received by villages B & D together = 125+ 210 = 335
S47. Ans. (e)
Sol.
Required percentage = (1500-250)/1500×100=83 1/3%
S48. Ans. (e)
Sol.
Required percentage = 25/5×100=500%
S49. Ans. (d)
Sol.
Required average = (60+125+25)/3=70
S50. Ans. (b)
Sol.
Required ratio = (60+125+25) : (200+50) = 210:250=21:25
| Related Post | |
| SBI Clerk 2024 | |
| SBI Clerk Previous Year Papers | SBI Clerk Mains Cut Off |
| SBI Clerk Salary | SBI Clerk Syllabus |




 Number Series Questions for SBI PO Exam
Number Series Questions for SBI PO Exam
 Simplification Questions for SBI PO Exam
Simplification Questions for SBI PO Exam
 Simplification Questions for SBI Clerk 2...
Simplification Questions for SBI Clerk 2...





