Direction (1-2): Study the information given below and answer the questions based on it:
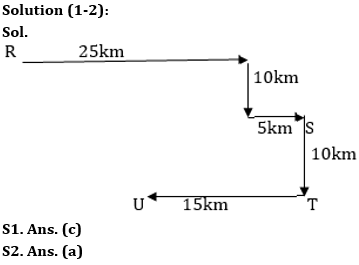
A person starts his journey from point R. He drives 25 km in east direction and then take a right turn and drives 10km. After taking left turn he reached point S after driving 5 km. Point T is 10 km to the south of S. From T, he is driving 15 km to the west to reach point U. Point S is to the southeast with respect to Point R.
Q1. If point K is 20km to the south of R, then what is the shortest distance between K and U?
(a) 20km
(b) 25km
(c) 15km
(d) 30km
(e) 35km
Q2. What is the direction of point U with respect to point S?
(a) South-west
(b) South-east
(c) East
(d) North-west
(e) None of these
Direction (3-5): Study the information given below and answer the questions based on it:
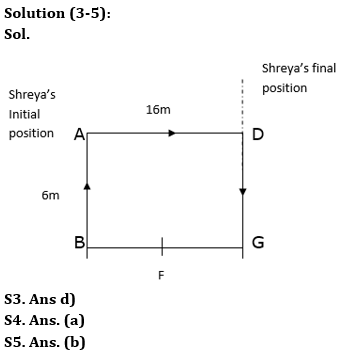
Point A is 6m to the north of point B. Point D is 16m to the east of point A. Point F is exactly in the middle of B and G. G is 6m south of D. Shreya is standing at point A, she walks 16m towards the east and then turns to her left and walks 6m.
Q3. In which direction is Shreya now with respect to her initial position?
(a) South-west
(b) South-east
(c) East
(d) North-east
(e) None of these
Q4. What is the shortest distance between D and F?
(a) 10m
(b) 15m
(c) 20m
(d) 30m
(e) 35m
Q5. What is the direction of point G with respect to point A?
(a) South-west
(b) South-east
(c) East
(d) North-west
(e) None of these
Direction (6-10): In the following questions assuming the given statement to be true, find which of the conclusion(s) among given conclusions is/are definitely true and then give your answers accordingly.
Q6. Statement: D > L ≥ J ≥ F ≤ U < G ≤ T
Conclusions: I. D > F
II. J < T
(a) If only conclusion I is true
(b) If only conclusion II is true
(c) If either conclusion I or II is true
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II is true
(e) If both conclusions I and II are true
Q7. Statement: L ≥ C > D ≥ E = R; O ≥ D ≥ Q
Conclusions: I. L > Q
II. O ≥ R
(a) If only conclusion I is true
(b) If only conclusion II is true
(c) If either conclusion I or II is true
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II is true
(e) If both conclusions I and II are true
Q8. Statements: N < D ≥ W; O ≥ T > G; N > O
Conclusions: I. W > T
II. D ≥ O
(a) If only conclusion I is true
(b) If only conclusion II is true
(c) If either conclusion I or II is true
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II is true
(e) If both conclusions I and II are true
Q9. Statement: Y < O < D > I = L > F
Conclusions: I. D < F
II. L > Y
(a) If only conclusion I is true
(b) If only conclusion II is true
(c) If either conclusion I or II is true
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II is true
(e) If both conclusions I and II are true
Q10. Statements: A < K < D > R; Y > D < S
Conclusions: I. Y > K
II. R < S
(a) If only conclusion I is true
(b) If only conclusion II is true
(c) If either conclusion I or II is true
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II is true
(e) If both conclusions I and II are true
Direction (11-15): In each of the questions below few statements are given followed by few conclusions. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read all the conclusions and then decide which of the given conclusions logically follows from the given statements, disregarding commonly known facts.
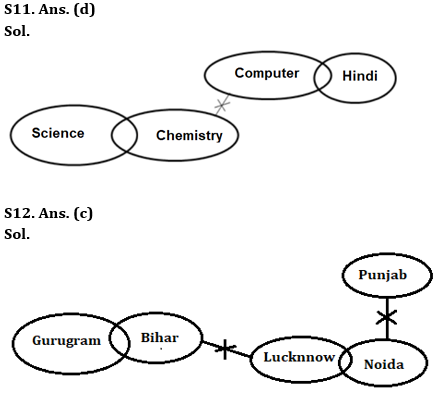
Q11. Statements: Only a few Science are Chemistry.
No Computer is Chemistry.
Some Computer is Hindi.
Conclusions: I. All Science can be Computer.
II. Some Computer are Science.
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Q12. Statements: Only a few Lucknow are Noida.
No Noida is Punjab.
Only a few Gurugram are Bihar.
No Bihar is Lucknow.
Conclusions: I. Some Noida are Gurugram.
II. No Gurugram are Noida.
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
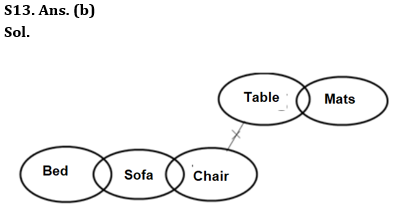
Q13. Statements: Some Tables are Mats.
Only a few Beds are Sofa.
Only a few Sofas are Chairs.
No Chair is Table.
Conclusions: I. No Chair is Bed.
II. All Sofa can never be Tables.
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
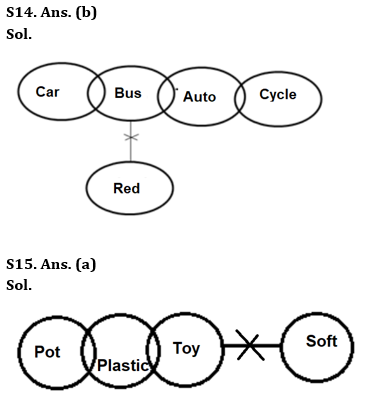
Q14. Statements: Only a few Cars are Buses.
No Bus is Red.
Only a few Buses are Autos.
Only a few Autos are Cycles.
Conclusions: I. Some Autos can never be Car.
II. All Autos being Bus is a possibility.
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
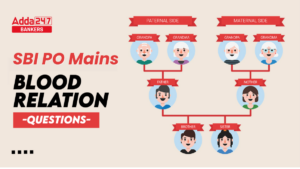
Q15. Statements: Only a few pots are Plastic.
Some Plastic are toy.
No toy is Soft.
Conclusions: I. Some pots are not Plastic.
II. Some pots are not Soft.
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Solutions
Solution (6-10):
S6. Ans. (a)
Sol. I. D > F – True
II. J < T – False
S7. Ans. (e)
Sol. I. L > Q – True
II. O ≥ R – True
S8. Ans. (d)
Sol. I. W > T – False
II. D ≥ O – False
S9. Ans. (d)
Sol. I. D < F – False
II. L > Y – False
S10. Ans. (e)
Sol. I. Y > K – True
II. R < S – True





 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 Important Blood Relation Questions for S...
Important Blood Relation Questions for S...





