Directions (1–5): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
In a certain code language,
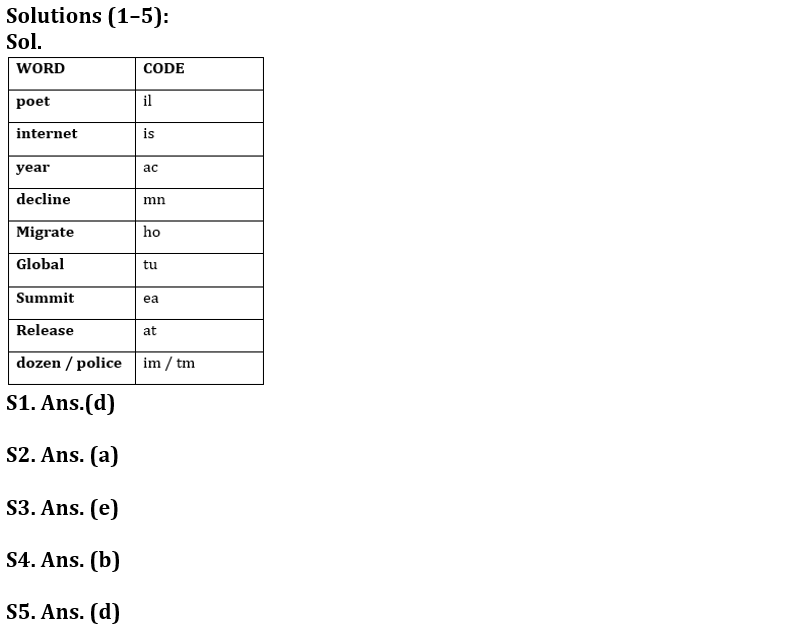
‘Dozen poet police internet’ is coded as ‘im il is tm,
‘Poet global summit year’ is coded as ‘ac tu il ea’
‘Year decline global release’ is coded as ‘ac tu at mn’
‘Internet migrate year decline’ is coded as ‘ho ac mn is’
Q1. How is ‘year’ coded in that code language?
(a) at
(b) tu
(c) is
(d) ac
(e) None of these
Q2. What does ‘is’ stand for?
(a) internet
(b) poet
(c) year
(d) police
(e) None of these
Q3. ‘im’ is the code for which of the following?
(a) dozen
(b) police
(c) migrate
(d) poet
(e) Can’t be determined
Q4. Which of the following is the code for ‘dozen police release decline’?
(a) tm tu mn at
(b) im tm at mn
(c) im ho is tu
(d) im at mn tu
(e) None of these
Q5. What is the code for ‘poet’?
(a) tu
(b) ea
(c) is
(d) il
(e) None of these
Directions (6-10): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below:
In a certain code language
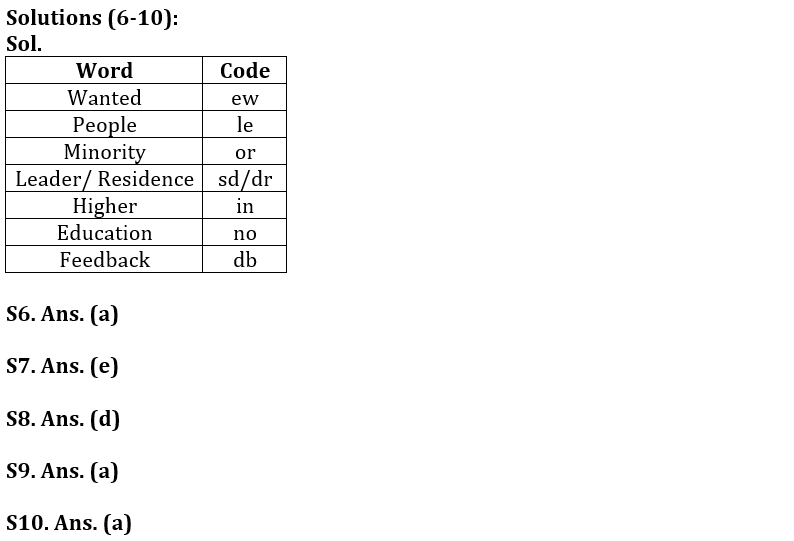
‘Wanted minority People’ is written as ‘ew or le’,
‘Education wanted higher’ is written as ‘in ew no’,
‘People leader residence’ is written as ‘sd le dr’,
‘Education feedback wanted’ is written as ‘db ew no’.
Q6. What is the code for ‘wanted’?
(a) ew
(b) or
(c) le
(d) no
(e) None of these
Q7. What is the code for ‘Leader’?
(a) sd
(b) le
(c) dr
(d) in
(e) Can’t be determined
Q8. What does ‘db’ stand for?
(a) Education
(b) residence
(c) minority
(d) feedback
(e) None of these
Q9. Which of the following may be the code for ‘people city residence’?
(a) le yt dr
(b) le yt ew
(c) sd dr le
(d) or le dr
(e) None of these
Q10. What is the code for ‘minority’?
(a) or
(b) le
(c) ew
(d) in
(e)None of these
Directions (11-15): In these questions, relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions.
Mark answer as
Q11. Statements: A≤M>G >K >D, M≤O< S, K<H
Conclusions: I. G < S II. A > D
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Q12. Statements: B ≥ E >L<O>R=U
Conclusions: I. B<L II. U=L
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Q13. Statements: X ≥ Q > F, A > F, R = M ≥ F
Conclusions: I. R > A II. X > F
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Q14. Statements: D ≤ G > K ≥ R > T, G ≤ E > W, R < Y
Conclusions: I. W ≥ D II. Y > T
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Q15. Statements: B ≥ K > G, M ≤ G, D = W ≥ G
Conclusions: I. D ≥ M II. K < W
(a) If only conclusion I follows.
(b) If only conclusion II follows.
(c) If either conclusion I or II follows.
(d) If neither conclusion I nor II follows.
(e) If both conclusions I and II follow.
Solutions
S11. Ans. (a)
Sol. I. G < S (true) II. A > D (false)
S12. Ans. (d)
Sol. I. B<L (false) II. U=L (false)
S13. Ans. (b)
Sol. I. R > A (false) II. X > F (true)
S14. Ans. (b)
Sol. I. W ≥ D (false) II. Y > T (true)
S15. Ans. (a)
Sol. I. D ≥ M (true) II. K < W (false)





 FCI Assistant Grade 3 Previous Year Ques...
FCI Assistant Grade 3 Previous Year Ques...
 FCI Manager Previous Year Question Paper...
FCI Manager Previous Year Question Paper...
 FCI DV Admit Card 2023 Out, Download FCI...
FCI DV Admit Card 2023 Out, Download FCI...




