Table of Contents
Directions (1-5): Study the given information carefully to answer the given question.
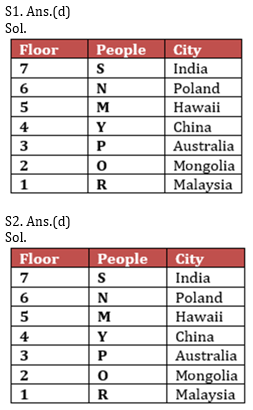
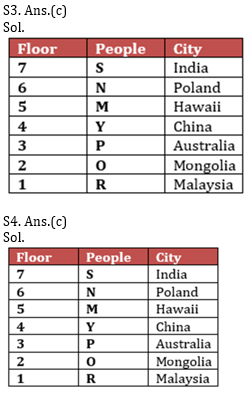
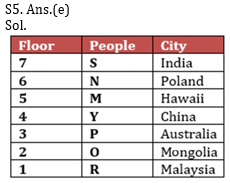
M, N, O, P, Y, R and S are seven friends live on seven different floors of a building, lower most floor of the building is numbered as 1, and topmost floor is numbered as 7, Also they belong to different countries i.e. Poland, Australia, India, Hawaii, Mongolia, China, and Malaysia (not necessarily in the same order).
Y lives on an even numbered floor. Two people live between Y and R, who doesn’t belong to Australia. The one who lives just above Y belongs to Hawaii. The one, who belongs to Poland, lives on an even numbered floor. Only one person lives between the ones who belong to Hawaii and P. R doesn’t live on 7th floor. The one who is from Hawaii is not N and neither lives on 1st and topmost floor. S belongs to India and lives just above N, who doesn’t live on 2nd floor. O belongs to Mongolia. The one, who belongs to China, lives on an even numbered floor below N. M doesn’t live below O’s floor.
Q1. Who among the following belongs to Australia?
(a) O
(b) N
(c) M
(d) P
(e) None of these
Q2. Which of the following combinations is true with respect to the given arrangement?
(a) Malaysia – O
(b) China– R
(c) Poland – S
(d) Australia – P
(e) None of these
Q3. N belongs to which country?
(a) Australia
(b) Hawaii
(c) Poland
(d) Mongolia
(e) India
Q4. Which of the following statements is true with respect to the given arrangement?
(a) M belongs to China
(b) Y lives on 3rd floor
(c) R belongs to Malaysia
(d) Only one people lives above S
(e) None of these
Q5. Who amongst the following lives on the floor numbered 2?
(a) M
(b) S
(c) None of these
(d) N
(e) The one, who belongs to Mongolia
Directions (6-10): Each of the question below consists of a question and two statements numbered I, and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question.
Q6. Who is tallest among five friends P, Q, R, S and T?
I. S is taller than R but just shorter than T.
II. T is shorter than P and Q is shorter than T.
(a) If statements I is sufficient to answer the question, but statement II by itself is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b)If statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question, but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) If statement either I or II is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) If both the statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) If both the statements I and II taken together are sufficient to answer the question.
Q7. How is K related to M?
I. M is Q’s father’s only sister.
II. N is mother K who is the daughter of O.
(a) If statements I is sufficient to answer the question, but statement II by itself is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b)If statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question, but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) If statement either I or II is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) If both the statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) If both the statements I and II taken together are sufficient to answer the question.
Q8. By using which statements, we can conclude “All hacking are theft”.
I. All hacking are security. No security is password. All security are theft.
II. All hacking are security. Some password are security. No password are theft.
(a) If statements I is sufficient to answer the question, but statement II by itself is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b)If statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question, but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) If statement either I or II is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) If both the statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) If both the statements I and II taken together are sufficient to answer the question.
Q9. How is ‘some’ written in a code language?
I. ‘some might procedure’ is written as ‘xm nu zx’ and ‘might would fight’ is written as ‘zx zy iz’ in that code language.
II. ‘some iconic procedure’ is written as ‘xm nu zm’ in that code language.
(a) If statements I is sufficient to answer the question, but statement II by itself is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b)If statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question, but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) If statement either I or II is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) If both the statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) If both the statements I and II taken together are sufficient to answer the question.
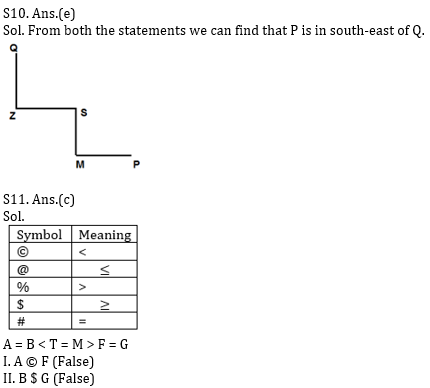
Q10. Point P is towards which direction from point Q?
I. Z is in south of Q and west of S, which is in north of M.
II. M is south of S and west of P.
(a) If statements I is sufficient to answer the question, but statement II by itself is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b)If statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question, but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) If statement either I or II is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) If both the statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) If both the statements I and II taken together are sufficient to answer the question.
Directions (11-15): In the following questions, the symbols @, ©, %, $ and # are used the following meaning as illustrated below:
‘A©B’ means ‘A is smaller than B’.
‘A@B’ means ‘A is either smaller than or equal to B’.
‘A%B’ means ‘A is greater than B’.
‘A $ B’ means ‘A is either greater than or equal to B’.
‘A#B’ means ‘A is equal to B’.
Now in each of these questions assuming the given statements to be true, find which of the two conclusions I and II given below them is/are definitely true? Give answer
Q11. Statements:
A # B © T # M % F # G
Conclusions:
I. A © F
II. B $ G
(a) if only Conclusion I is true.
(b) if only Conclusion II is true.
(c) if either Conclusions I or II is true.
(d) if neither Conclusions I nor II is true.
(e) if both Conclusions I and II are true.
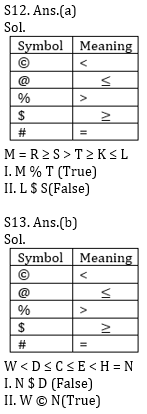
Q12. Statements:
M # R $ S % T $ K @ L
Conclusions:
I. M % T
II. L $ S
(a) if only Conclusion I is true.
(b) if only Conclusion II is true.
(c) if either Conclusions I or II is true.
(d) if neither Conclusions I nor II is true.
(e) if both Conclusions I and II are true.
Q13. Statements:
W © D @ C @ E © H # N
Conclusions:
I. N $ D
II. W © N
(a) if only Conclusion I is true.
(b) if only Conclusion II is true.
(c) if either Conclusions I or II is true.
(d) if neither Conclusions I nor II is true.
(e) if both Conclusions I and II are true.
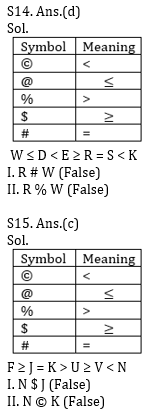
Q14. Statements:
W @ D © E $ R # S © K
Conclusions:
I. R # W
II. R % W
(a) if only Conclusion I is true.
(b) if only Conclusion II is true.
(c) if either Conclusions I or II is true.
(d) if neither Conclusions I nor II is true.
(e) if both Conclusions I and II are true.
Q15. Statements:
F $ J # K % U $ V © N
Conclusions:
I. N $ J
II. N © K
(a) if only Conclusion I is true.
(b) if only Conclusion II is true.
(c) if either Conclusions I or II is true.
(d) if neither Conclusions I nor II is true.
(e) if both Conclusions I and II are true.
Practice More Questions of Reasoning for Competitive Exams:
Reasoning for Competitive Exams |
Reasoning Ability Quiz For ECGC PO 2021- 19th February |
Reasoning Ability Quiz For ECGC PO 2021- 18th February |
ECGC PO Study Plan 2021 |
Solutions
S6. Ans.(e)
Sol. Using both statements together, P is the tallest person.
From Statement I- T>S>R
From statement II- P>T>Q
From both statements- P>T>S>R/Q>R/Q
S7. Ans.(d)
S8. Ans.(a)
S9. Ans.(d)
Sol. From statement I- code of ‘some’ may be xm/nu.
From statement II- we cannot find exact code of ‘some’.
Practice with Crash Course and Online Test Series for ECGC PO 2021:
- ECGC Online Coaching Classes for Probationary Officier 2021
- ECGC PO Mock Tests 2021 – Banking Online Test Series (With Solutions) by Adda247
- ECGC PO 2021 Complete eBooks Kit (English Medium)
Click Here to Register for Bank Exams 2020 Preparation Material




 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 Importance of Descriptive Questions in S...
Importance of Descriptive Questions in S...





