Direction (1-5): Study the following data carefully and answer the questions accordingly.
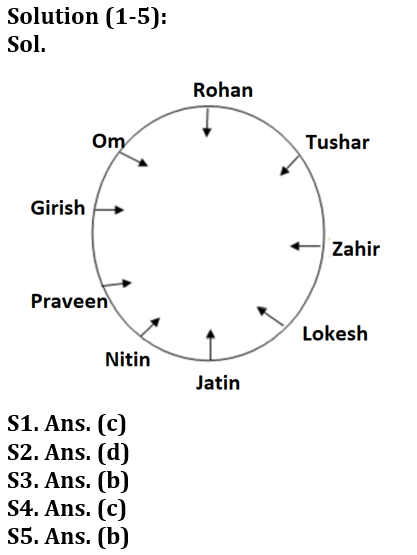
Nine people are sitting around a circular table facing the center. Three people sit between Jatin and Rohan. One person sits between Girish and Rohan. More than one person sits between Jatin and Girish, when counted from both sides, right and left of Jatin. Nitin sits second to the right of Girish. Zahir is not sitting immediate right of Tushar. Lokesh is an immediate neighbor of Jatin. One person sits between Tushar and Lokesh. One person sits between Praveen and Om who is not an immediate neighbor of Nitin.
Q1. Who sits third to the right of Zahir?
(a) Rohan
(b) Lokesh
(c) Om
(d) Jatin
(e) None of these
Q2. Who among the following are immediate neighbors of Nitin?
(a) Zahir, Girish
(b) Praveen, Om
(c) Jatin, Lokesh
(d) Praveen, Jatin
(e) None of these
Q3. If Rohan is related to Girish and Jatin is related to Zahir then Tushar is related to_____?
(a) Praveen
(b) Om
(c) Girish
(d) Nitin
(e) None of these
Q4. What is the position of Lokesh from Praveen?
(a) Fifth to the right
(b) Third to the left
(c) Third to the right
(d) Second to the left
(e) None of these
Q5. Find the correct statement/statements from the following.
I. One person sits between Rohan and Zahir, when counted right of Zahir.
II. Nitin and Girish are immediate neighbors.
III. Lokesh sits second to the left of Om.
(a) Both I and III
(b) Only I
(c) Both I and II
(d) All are correct
(e) None is correct
Directions (6-10): In these questions, relationship between different elements is shown in the statements. These statements are followed by two conclusions. Mark answer
(a) if only conclusion I is true.
(b) if only conclusion II is true.
(c) if either conclusion I or II is true.
(d) if neither conclusion I nor II is true.
(e) if both conclusion I and II are true.
Q6. Statements: A>B, D≤E, C≥F=G, B≤C=D
Conclusions: I. B≥G
II. E≥G
Q7. Statements: T>S≤Q, T≥U=V, H≥T
Conclusions: I. U≤H
II. S<H
Q8. Statements: A>B≥L, R>B=H
Conclusions: I. A<L
II.R>L
Q9. Statements: P>K=L, P≤S<Q, T>K
Conclusions: I.Q>K
II.Q<T
Q10. Statements: P<H, V≥S>H, N≥V
Conclusions: I. N≥P
II. S>P
Solutions






 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 30 Days Study Plan to Crack SBI Clerk 20...
30 Days Study Plan to Crack SBI Clerk 20...





