Q1. Average age of Sohan, Mohini and their twin’s daughter is 22.5 years and average age of Mohini, and her twin’s daughter is 52/3 years. If average age of Sohan and Mohini is 37 years, then find average age of Sohan and his twin’s daughter?
(a) 24 years
(b) 16 years
(c) 19 years
(d) 18 years
(e) 21 years
Q2. A chemical shop owner has 40 liters of liquid ‘A’ and he sells 10 liters of liquid ‘A’ and replaced same quantity of water. He repeats same process one more time further, find quantity of liquid ‘A’ is how much more than water in final mixture?
(a) 5 liters
(b) 12 liters
(c) 20 liters
(d) 17.5 liters
(e) 25 liters
Q3. The diagonal of rectangle which length 12 cm and breadth 5 cm are equal to hypotenuse of a right – angle isosceles tringle. Find the area of rectangle is how much more than ( in cm sq.) that of area of right – angle isosceles tringle?
(a) 16.75
(b) 17.25
(c) 17.75
(d) 17.50
(e) 18.25
Q4. The ratio of investment of Anurag and Ayush is 2 : 3 and out of total profit of Rs. 76000 shares of Ayush is Rs. 36000. Find the ratio of time period for which Anurag and Ayush invested their capital respectively?
(a) 3 : 2
(b) 6 : 5
(c) 4 : 3
(d) None of these
(e) 7 : 6
Directions (6-10): In the given questions, two quantities are given, one as ‘Quantity I’ and another as ‘Quantity II’. You must determine relationship between two quantities and choose the appropriate option:
Q6. Quantity I – 2x² – 31x + 84 = 0
Quantity II – 3y² + y – 2 = 0
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation
Q7. Quantity I – On selling 21 bottles at Rs. 1620, there is a profit equal to the cost price of 6 bottles. The cost price of a bottle is
Quantity II – A, B and C completed a work costing Rs. 2400. A, B and C can complete the work alone in 12, 20 and 30 days respectively. If A, B and C together finish the work, then find the half of per day wage of B?
(a) Quantity I < Quantity II
(b) Quantity I > Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation
Q8. Quantity I – 6499 + 3601 × 14.989 – 8799.9+97.334 =?, approximate value of question mark (?).
Quantity II – Ram invested Rs. 30000 at the rate of X% for two years on compound interest and gets total amount of Rs. 39675. If Ram invested same amount at the rate of (X + 5)% for two years on compound interest, then find four times of interest that Ram will get?
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation
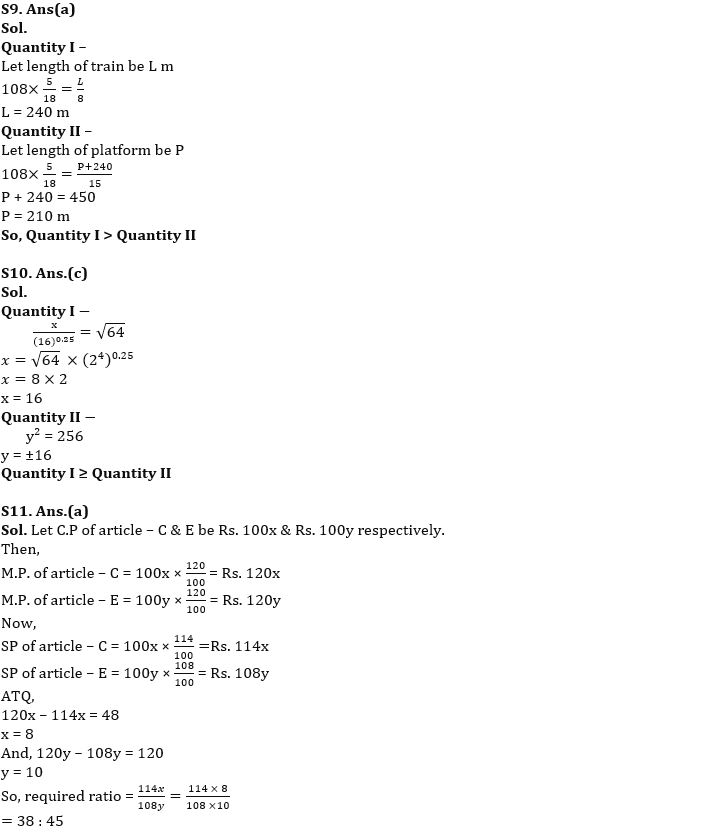
Q9. A train running at the speed of 108 km/hr crosses a pole in 8 sec.
Quantity I – Length of train.
Quantity II – Length of platform which train crosses in 15 sec.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation
Q10. Quantity ![]()
Quantity II – y² = 256
(a) Quantity I < Quantity II
(b) Quantity I > Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or no relation
Directions (11-15): Study the line chart given below and answer the following questions.
Line chart shows the markup percentage with respect to cost price and profit percentage of five articles.
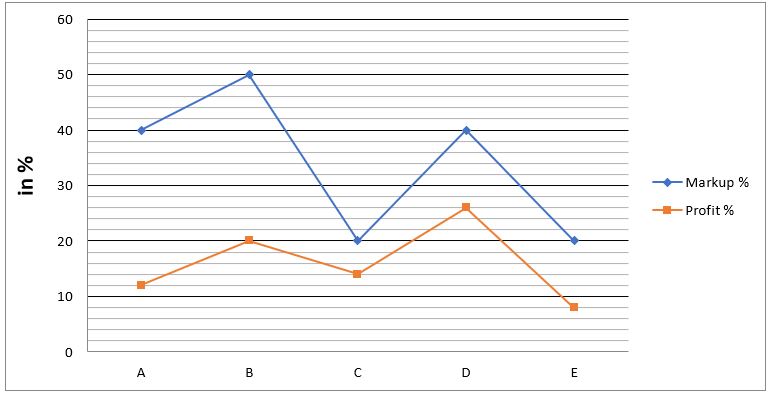
Q11. If discount allowed on article-C & E is Rs.48 & Rs.120 respectively, then find ratio of selling price of article-C to selling price of article-E.
(a) 38 : 45
(b) 21 : 22
(c) 5 : 12
(d) 27 : 35
(e) 2 : 3
Q12. If ratio of cost price of article-A to that of article-E is 1 : 2, then find difference between selling price of article-A & article-E is what percent of marked price of article-E?
(a) 40⅓%
(b) 48⅓%
(c) 35⅔%
(d) 43⅓%
(e) None of the above.
Q13. If discount allowed on article-B is halved, then find the change in profit percentage.
(a) 10%
(b) 20%
(c) 15%
(d) 25%
(e) 5%
Q14. If marked price of article-C is 60% more than that of article-B and difference between discount allowed on article-B & article-C is Rs.72, then find average of cost price of article-C & B.
(a) Rs.600
(b) Rs.300
(c) Rs.500
(d) Rs.700
(e) Rs.400
Q15. If cost price of article-D is 25% of marked price of article-E, then find selling price of article-D is what percent of selling price of article-E?
(a) 25%
(b) 60%
(c) 15%
(d) 50%
(e) 35%
Solutions




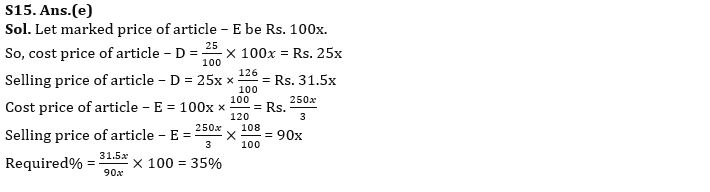





 Quantitative Aptitude Quiz For Bank Main...
Quantitative Aptitude Quiz For Bank Main...
 Quantitative Aptitude Quiz For Bank Foun...
Quantitative Aptitude Quiz For Bank Foun...




