Directions (1-4): The following questions are accompanied by two statements I and II. You have to determine which statements(s) is/are sufficient/necessary to answer the questions.
Q1. Find the sum of present age of X & Z?
I. Four years ago, average age of X, Y and Z was 16 years while age of X, Y and Z is in arithmetic progression.
II. Average of present age of X and Z is same as present age of Y while Y is four years younger than Z.
(a) Statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement II alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b) Statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) Both the statements taken together are necessary to answer the questions, but neither of the statements alone is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) Either statement I or statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question.
(e) Statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
Q2. Is Rahul meet Prabhat at half of the distance on a circular track (48km) if they both started to move at same time in same direction?
I. Speed of Prabhat is 24km/hr more than speed of Rahul.
II. Prabhat’s speed is 200% more than that of Rahul
(a) Statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement II alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b) Either statement I or statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question.
(c) Both the statements taken together are necessary to answer the questions, but neither of the statements alone is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) Statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) Statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
Q3. Find number of yellow balls in a box which contains 3 black balls and 7 red and yellow balls.
I. Probability of selecting two yellow balls from the box is 2/15
II. Probability of selecting one red and black ball is ⅕.
(a) Statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement II alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(b) Statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) Both the statements taken together are necessary to answer the questions, but neither of the statements alone is sufficient to answer the question.
(d) Either statement I or statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question.
(e) Statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
Q4. Find number of pens sold by retailer if he earns total 37.5% profit on selling some pens and some pencils.
I. Ratio between pen sold to pencil sold is 2 : 3 while ratio between cost price of pen to pencil is 3 : 2.
II. On selling a pen and a pencil, he earns 25% and 50% profit respectively.
(a) Both the statements taken together are necessary to answer the questions, but neither of the statements alone is sufficient to answer the question.
(b) Statements I and II taken together are not sufficient to answer the question.
(c) Statement II alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement I alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(d) Statement I alone is sufficient to answer the question but statement II alone is not sufficient to answer the question.
(e) Either statement I or statement II by itself is sufficient to answer the question.
Directions (5-6): In the given questions, two quantities are given, one as Quantity I and another as Quantity II. You have to determine relationship between two quantities and choose the appropriate option.
Q5. There are three vessel A, B and C. Vessel A contains mixture of milk and water in ratio 3 : 1. Vessel B contains 20 litres of pure water while vessel C contains 30 litres of pure milk. Half of the content of vessel A is first poured into vessel B. Then content of vessel B is poured into vessel C and finally contents of vessel C is poured into vessel A. The final ratio of milk and water in vessel A is 9 : 4.
Quantity I: Initial quantity of mixture in vessel A.
Quantity II: 80 litres.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q6. 20 men can complete a work in 12 days. 5 women are as efficient as 3 men. 4 men and 10 women started working and they already worked for 8 days.
Quantity I: Additional number of women required to complete the remaining work in 10 days.
Quantity II: Additional number of men required to complete the remaining work in either 8 or less than 8 days.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q7. Quantity I — Time taken by A to complete a work alone if A can complete a work in 5 more days than B while A does the same work in 9 more days than C. If A and B can complete the whole work in same time as time taken by C alone to do the whole work.
Quantity II — Time taken by 8 men and 14 women to reap 7/12 part of 360 hectare land by working 7 hrs per day if 6 men and 10 women can reap 5/12 part of the land in 15 days by working 6 hrs per day. It is also given that work of 2 men is equal to that of 3 women.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q8. Quantity I — Difference between the speeds of P and Q if 2 places A and B are 60 km apart. P and Q start from A at same time & meet 1st time at a place 12 km from B & they reach A after immediate return from B. The speed of slower person is 48 km/hr.
Quantity II — Average speed of train if a distance of 600 km is to be covered in 2 parts. In 1st phase 120 km is travelled by train and rest by car and it took total of 8 hrs, but if 200 km is covered by train and rest by car it takes 20 min more.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q9. Quantity I — Cost price of motor bike if a man promises to pay the price of the motorbike in 3 equal annual installments of 10,800 Rs. at the compound interest rate of 20% per annum.
Quantity II — 240% of the value of each installment if a man borrowed a sum of Rs. 25220 from a bank and promise to pay the amount in 3 equal installments at the compound interest rate of 5% per annum.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q10. Quantity I — Value of x, if ABCD is a rectangle and AB= 10 unit, AD= 6 unit.
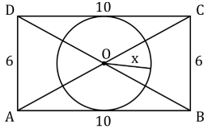
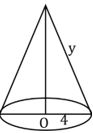
Quantity II — value of y, if volume of the cone is 16π unit3
Radius = 4 unit
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Solutions











 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 RRB NTPC Exam Date 2025 Soon, Check Expe...
RRB NTPC Exam Date 2025 Soon, Check Expe...





