Directions (1-5): In each question below only one number is missing. Please understand the data carefully and find the value of question mark(?).
Q1. 14, 17.5, ?, 24.5, 28, 31.5
(a) 19.5
(b) 21
(c) 22.5
(d) 18.5
(e) 22
Q2. 10, 12, 27, 85, ?, 1731
(a) 1122
(b) 754
(c) 964
(d) 345
(e) 465
Q3. 24, 27, ?, 30, 18, 33
(a) 28
(b) 25
(c) 21
(d) 36
(e) 26
Q4. 15, 30, 10, 40, 8, ?
(a) 48
(b) 72
(c) 32
(d) 64
(e) 56
Q5. ?, 314, 294, 264, 224, 174
(a) 302
(b) 304
(c) 324
(d) 320
(e) 308
Directions (6-10): Please read the data carefully and answer the questions given below.
In a school there are total 250 teachers of Maths, Physics, English and Computer in which the ratio of male teachers to female teachers is 3:2. The total number of Maths teacher are 80 in which male and female are in the ratio of 3:1. The total number of Physics teacher are 60 while the difference between the male Physics teacher and female Physics teacher is 30(male teacher>female teacher). The total number of female English teacher is 10 more than the number of male Physics teacher and the total number of English teachers is 75.
Q6. Find the number of female Computer teachers is what percent of total Maths teacher in school.
(a) 12.5%
(b) 20%
(c) 87.5%
(d) 62.5%
(e) 10%
Q7. Find the ratio of number of female English teachers to number of male Physics teachers.
(a) 11: 6
(b) 8: 5
(c) 7: 6
(d) 12: 7
(e) 11: 9
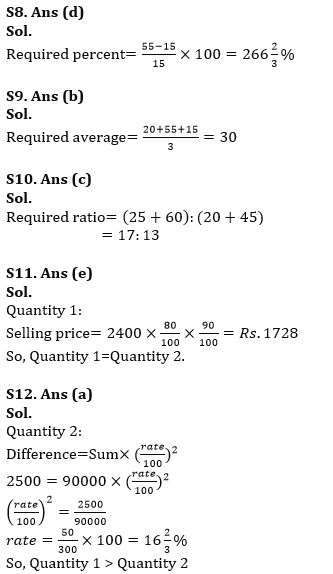
Q8. Find number of female English teachers are what percent more/less than number of female Physics teachers.
(a) 33⅓%
(b) 233⅓%
(c) 166⅔%
(d) 266⅔%
(e) 366⅔%
Q9. Find the average of number of female teachers of English, Math and Physics.
(a) 20
(b) 30
(c) 25
(d) 10
(e) 15
Q10. Find the ratio of male teachers of Computer and Maths together to male teachers of English and Physics together.
(a) 13: 9
(b) 15: 11
(c) 17: 13
(d) 15: 13
(e) 17: 11
Directions (11-15): In each questions below two quantities, Quantity 1 and Quantity 2, are given. Please solve the question, compare the two quantities and mark the answer accordingly.
Q11. Quantity 1: Selling price of an item (in Rs.), if shopkeeper allows two successive discounts of 20% and 10% on an item marked at Rs. 2400.
Quantity 2: Rs.1728
(a) Quantity 1 > Quantity 2
(b) Quantity2 ≥ Quantity 1
(c) Quantity 1 ≥ Quantity2
(d) Quantity 2 > Quantity 1
(e) Quantity 1=Quantity 2 or no relation can be established
Q12. Quantity 1: 18%
Quantity 2: Rate of interest, the difference between compound interest and simple interest on a sum of Rs.90000 for a period of two years is Rs.2500.
(a) Quantity 1 > Quantity 2
(b) Quantity2 ≥ Quantity 1
(c) Quantity 1 ≥ Quantity2
(d) Quantity 2 > Quantity 1
(e) Quantity 1=Quantity 2 or no relation can be established
Q13. Quantity 1: price (in Rs.) he/she should sold the mixture in order to gain a profit of 10%, A shopkeeper mix two varieties of rice costing Rs.30/kg and Rs.42/kg in the same ratio and sold to customer.
Quantity 2: Rs.41.4
(a) Quantity 1 > Quantity 2
(b) Quantity2 ≥ Quantity 1
(c) Quantity 1 ≥ Quantity2
(d) Quantity 2 > Quantity 1
(e) Quantity 1=Quantity 2 or no relation can be established
Q14. Quantity 1: x; x²+9x+20=0
Quantity 2: y; 2y²+15y+28=0
(a) Quantity 1 > Quantity 2
(b) Quantity2 ≥ Quantity 1
(c) Quantity 1 ≥ Quantity2
(d) Quantity 2 > Quantity 1
(e) Quantity 1=Quantity 2 or no relation can be established
Q15. Quantity 1: x; x=√256
Quantity 2: y; y²=256
(a) Quantity 1 > Quantity 2
(b) Quantity2 ≥ Quantity 1
(c) Quantity 1 ≥ Quantity2
(d) Quantity 2 > Quantity 1
(e) Quantity 1=Quantity 2 or no relation can be established
Solutions









 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 Punjab and Sind Bank LBO Exam Date 2025 ...
Punjab and Sind Bank LBO Exam Date 2025 ...





