Q1. What is the cost of 100 Rs face value debenture with coupon 13%, maturity is 6 years, redemption at 6% premium and realizable amount is Rs 97.50 and tax is 38%.
(a) 9.25%
(b) 9.56%
(c) 9.13%
(d) 9.31%
(e) 9.49%
Q2. Market portfolio contains –
(a) Frequently traded securities in the stock market
(b) All the securities in proportion to their market capitalization
(c) All securities listed in the specific group of a stock exchange
(d) The securities having large volumes in terms of number of transactions and market capitalization
(e) None of the above
Q3. Which of the following is not an assumption of CAPM
(a) Capital market are perfect
(b) Lending rate is more than borrowing rate
(c) No individual is capable of affecting market
(d) Homogeneous expectations
(e) All the above are assumptions
Q4. A change in YTM affects those bonds with a higher YTM _______________it affects bonds with a lower YTM
(a) Less than
(b) More than
(c) Same as
(d) Either of (A) or (C) above
(e) Either of (B) or (C) above
Q5. The price of the share will increase if
(a) The dividend increases
(b) The required rate of return increases
(c) The growth rate increases
(d) Both (B) and (C) above
(e) All of (A), (B) and (C) above
Q6. Low assets turnover ratio may indicate
(a) Low assets
(b) High cost of maintenance
(c) Idle assets
(d) Higher sales
(e) Both (B) and (C) above
Q7. Which of the following would affect the dividend yield directly?
(a) Retention ratio
(b) Book value per share
(c) Face value of a share
(d) The cost of equity capital
(e) Debt equity ratio
Q8. Equity multiplier is defined in DU Pont Analysis as
(a) Earnings per share / Market price per shares
(b) Earnings per share / Book value of shares
(c) Profit after tax/ Net worth
(d) Average assets/Average Equity
(e) None of the above
Q9. How does financial statement analysis help in understanding financial statements? –
(a) Window dressing
(b) Price level changes
(c) Correlation among ratios
(d) Differences in accounting policies
(e) None of the above
Q10. What is the total cost of maintaining an inventory of 200 units if the carrying cost per unit is Rs. 3, the cost per order is Rs 10 and there are 4 orders per year?
(a) 340
(b) 600
(c) 640
(d) 800
(e) 840
Solutions
S1.Ans.(d)
Sol.
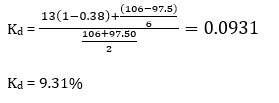
S2.Ans.(b)
Sol. Market portfolio contains all the securities in proportion to their market capitalization
S3.Ans.(b)
Sol. CAPM assumes the Lending rate and borrowing rate to be the same and equal to risk free rate
S4.Ans.(b)
Sol. As per bond pricing theorems, a change in YTM affects those bonds with a higher YTM more than it affects bonds with a lower YTM
S5.Ans.(c)
Sol.

S6.Ans.(c)
Sol. A low asset turnover ratioindicates it is not efficiently using its assets to generate sales.
S7.Ans.(a)
Sol. The retention ratio is the proportion of earnings kept back in the business as retained earnings. The retention ratio refers to the percentage of net income that is retained to grow the business, rather than being paid out as dividends. It is the opposite of the payout ratio, which measures the percentage of earnings paid out to shareholders as dividends.
The formula for the retention ratio is: Retention Ratio = (Net Income – Dividends) / Net Income
On a per-share basis, the retention ratio can be expressed as 1 – (Dividends per share / EPS).
S8.Ans.(d)
Sol.

S9.Ans.(e)
Sol. All the given options are the problems encountered in the financial analysis
S10.Ans.(a)
Sol.
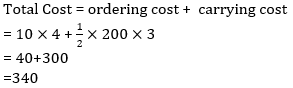





 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 Adda247 Project Rockstar, Check Video Ed...
Adda247 Project Rockstar, Check Video Ed...





