Table of Contents
Number series is an important topic in bank exams and it is widely asked under the Quantitative Aptitude section. This topic evaluates a candidate’s logical thinking, numerical ability and problem-solving speed. Understanding the fundamentals and strategies for solving number series questions effectively is essential for success in exams like SBI Clerk, IBPS PO, RBI Assistant and other banking recruitment tests.
Number Series for Bank Exams
A number series is a sequence of numbers arranged in a particular order based on a specific pattern. The task is to find the logic behind the pattern and predict the next number(s), find the missing number(s) or find the wrong number in the series. This type of question tests how well candidates can identify patterns and apply mathematical rules quickly.
Types of Number Series Questions
- Arithmetic Series: In this series, a constant number is added or subtracted to each term to produce the next term. Example: 5, 10, 15, 20, ? (Pattern: Adding 5 each time)
- Geometric Series: Each term in the series is multiplied or divided by a constant number to get the next term. Example: 3, 6, 12, 24, ? (Pattern: Multiplying by 2 each time)
- Square/Cube Series: This involves numbers that are squares or cubes of consecutive integers. Example: 1, 8, 27, 64, ? (Pattern: Cubes of 1, 2, 3, 4)
- Fibonacci Series: Each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. Example: 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, ? (Pattern: Adding the last two terms)
- Mixed Series: These are complex series where a combination of different operations or alternating patterns is used. Example: 2, 4, 6, 11, 14, 20, ? (Pattern: Alternating addition and multiplication)
- Pattern-Based Series: Series based on a defined rule involving patterns such as alternate operations, skipping numbers, etc. Example: 3, 7, 15, 31, ? (Pattern: Doubling the previous term and subtracting 1)
Number Series Questions for Bank Exams
Directions (1 – 10): In each of these questions a number series is given. In each series only one number is wrong. Find out the wrong number.
Q1. 15, 22, 6, 30, – 2, 38, -10
(a) 15
(b) 22
(c) 6
(d) -2
(e) 38
Q2. 18, 5, 9, 9.5, 23, 54.5, 164.5
(a) 54.5
(b) 18
(c) 5
(d) 9
(e) 164.5
Q3. 102, 158, 218, 282, 350, 422, 500
(a) 102
(b) 218
(c) 350
(d) 500
(e) 422
Q4. 72, 52, 42, 30, 20, 12, 6
(a) 72
(b) 42
(c) 30
(d) 6
(e) 52
Q5. 125, 164, 284, 484, 764, 1124
(a) 120
(b) 125
(c) 116
(d) 108
(e) 136
Q6. 375, 384, 394, 410, 434, 468, 514
(a) 384
(b) 514
(c) 394
(d) 375
(e) 434
Q7. 248, 250, 279, 295, 420, 456, 799.
(a) 279
(b) 250
(c) 295
(d) 456
(e) 799
Q8. 16, 22, 28, 40, 56, 76, 100
(a) 22
(b) 28
(c) 56
(d) 16
(e) 40
Q9. 6, 8, 18, 57, 232, 1165, 6996
(a) 57
(b) 8
(c) 6996
(d) 1165
(e) 6
Q10. 15, 14, 26, 75, 296, 1485, 8844
(a) 15
(b) 75
(c) 296
(d) 26
(e) 1485
Directions (11 – 20): In each of these questions a number series is given. Find what comes at the place of question (?) mark.
Q11. 11, 13, 17, 25, 41, ?
(a)73
(b)79
(c)82
(d)90
(e)68
Q12. 21, ?, 46, 66, 91, 121
(a)39
(b)31
(c)29
(d)27
(e)33
Q13. 3, 6, 14, 38, ?, 206
(a)154
(b)126
(c)86
(d)112
(e)72
Q14. 2, 12, ?, 240, 720, 1440
(a)72
(b)84
(c)36
(d)60
(e)48
Q15. 3, 6, ?, 42, 123, 366
(a)12
(b)24
(c)15
(d)18
(e)21
Q16. 11, 16.5, 22, 27.5, ?, 38.5
(a)34.5
(b)32
(c)30.5
(d)31.5
(e)33
Q17. 390, 300, 244, 214, ?, 200
(a)210
(b)208
(c)206
(d)204
(e)202
Q18. ?, 45, 36, 43, 34, 41
(a)38
(b)28
(c)36
(d)54
(e)27
Q19. 7, 25, ?, 69, 99, 137
(a)39
(b)58
(c)62
(d)45
(e)57
Q20. 761, 592, 448, 327, ?, 146
(a)302
(b)264
(c)292
(d)276
(e)227
Directions (21-30): What will come in place of question (?) mark in the following number series?
Q21. 25, 33, 46, 69, 112, ?
(a) 175
(b) 180
(c) 185
(d) 190
(e) 195
Q22. ? , 5, 12, 39, 160, 805
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 5
(e) 8
Q23. 11, 24, 41, 62, ?, 116
(a) 81
(b) 86
(c) 87
(d) 93
(e) 103
Q24. 122, 114, 98, 66, ?, -126
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 2
(d) 11
(e) 17
Q25. 56, 72, 90, 110, ?, 156
(a) 132
(b) 90
(c) 73
(d) 93
(e) 87
Q26. 567, 571, ? , 623, 687, 787
(a) 615
(b) 599
(c) 587
(d) 601
(e) 593
Q27. 167, 118, 76, 42, ?, -4
(a) 17
(b) 14
(c) 18
(d) 16
(e) 25
Q28. ?, 120, 134, 160, 204, 272
(a) 112
(b) 104
(c) 106
(d) 114
(e) 100
Q29. 5, ? , 2067, 2411, 2537, 2565
(a) 1337
(b) 1327
(c) 1317
(d) 1307
(e) 1347
Q30. 427, ? , 366, 73.2, 292.8, 97.6
(a) 51
(b) 41
(c) 61
(d) 71
(e) 31
Directions (31 -45): In each of these questions a number series is given. In each series, only one number is wrong. Find out the wrong number.
Q31. 404, 388, 366, 332, 292, 244, 188
(a) 188
(b) 366
(c) 244
(d) 292
(e) 332
Q32. 512, 255, 127, 63, 31, 15, 7
(a) 15
(b) 31
(c) 127
(d) 512
(e) 63
Q33. 521, 563, 613, 670, 734, 805, 883
(a) 613
(b) 805
(c) 734
(d) 563
(e) 521
Q34. 137, 149, 179, 235, 325, 457, 630
(a) 630
(b) 149
(c) 325
(d) 457
(e) 179
Q35. 312, 314, 330, 366, 430, 530, 674
(a) 430
(b) 314
(c) 674
(d) 366
(e) 312
Q36. 0.5, 3.5, 21, 105, 420, 1260, 2500
(a) 21
(b) 105
(c) 2500
(d) 420
(e) 3.5
Q37.2249, 2240, 2215, 2166, 2085, 1964, 1796
(a) 1796
(b) 2166
(c) 2085
(d) 2240
(e) 1964
Q38. 17, 35, 66, 126, 244, 478, 944
(a) 35
(b) 244
(c) 478
(d) 17
(e) 66
Q39. 114, 154, 202, 258, 322, 394, 478
(a) 394
(b) 478
(c) 202
(d) 322
(e) 258
Q40. 596, 611, 628, 647, 670, 699, 730
(a) 611
(b) 670
(c) 628
(d) 730
(e) 596
Q41. 130, 160, 176,301, 337, 680, 744
(a) 130
(b) 337
(c) 301
(d) 160
(e) 176
Q42. 711, 722, 744, 777, 821, 876, 940
(a) 821
(b) 940
(c) 744
(d) 722
(e) 876
Q43. 3, 4, 9, 28, 113, 566, 3396
(a) 113
(b) 566
(c) 3396
(d) 3
(e) 4
Q44. 444, 448, 474, 489, 613, 648, 990
(a) 474
(b) 990
(c) 448
(d) 444
(e) 613
Q45. 125, 343, 81, 1331, 169, 3375, 289
(a) 125
(b) 343
(c) 1331
(d) 289
(e) 81
Tips for Solving Number Series Questions
- Observe Differences: Check the difference between consecutive terms to see if it follows an arithmetic or increasing/decreasing pattern.
- Look for Multiplication or Division: If differences don’t show a pattern, try multiplication or division between terms.
- Check for Squares and Cubes: Identify if the series consists of perfect squares, cubes, or a combination.
- Alternate Patterns: Verify if there are two or more sub-patterns alternating throughout the series.
- Mixed Series: For complex series, consider the possibility of mixed patterns or sequences derived from known series like Fibonacci.
- Practice Time Management: Spend a reasonable amount of time on each question. If a pattern isn’t clear within 30-40 seconds, move on and return later if time permits.
Solutions:
S1. Ans(a)
Sol:
Pattern of series
Wrong number = 15
14+8=22
22-16=6
6+24=30
30 -32= -2
-2+40 =38
38-48 = -10
S2. Ans (a)
Sol. Pattern of series
Wrong number = 54.5
18×0.5-4=5
5×1+4=9
9×1.5-4=9.5
9.5×2+4=23
23×2.5-4=53.5
53.5×3+4=164.5
S3. Ans (d)
Sol. Pattern of series
Wrong number = 500
102+56=158
158+60=218
218+64=282
282+68=350
350+72=422
422+76=498
S4. Ans (e)
Sol. Pattern of series
Wrong number = 52
8×9=72
7×8=56
6×7=42
5×6=30
4×5=20
3×4=12
2×3=6
S5. Ans. (b)
Sol. Pattern of series
Wrong number = 125
124+40×1=164
164+40×3=284
284+40×5=484
484+40×7=764
764+40×9=1124
S6. Ans.(d)
Sol. Wrong number = 375.
there will be 378 in place of 375.
S7. Ans.(b)
Sol. Wrong number = 250.
there will be 252 in place of 250.
S8. Ans(a)
Sol.
Wrong number = 22
Pattern of series –
16+4=20
20+8=28
28+12=40
40+16=56
56+20=76
76+24=100
S9. Ans(e)
Sol.
Wrong number = 6
Pattern of series –
7×1+1=8
8×2+2=18
18×3+3=57
57×4+4=232
232×5+5=1165
1165×6+6=6996
S10. Ans (e)
Sol.
Wrong number = 1485
Pattern of series –
151-1 = 14
142-2 = 26
263-3 = 75
754-4 = 296
2965-5 = 1475
1475 ×6-6=8844
S11. Ans (a)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
11+2=13
13+4=17
17+8=25
25+16=41
41+32=73
S12. Ans (b)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
21+10=31
31+15=46
46+20=66
66+25=91
91+30=121
S13. Ans (c)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
3+22-1=6
6+32-1=14
14+52-1=38
38+72-1=86
86+112-1=206
S14. Ans (d)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
2×6=12
12×5=60
60×4=240
240×3=720
720×2=1440
S15. Ans (c)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
3×3-3=6
6×3-3=15
15×3-3=42
42×3-3=123
123×3-3=366
S16. Ans (e)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
11+5.5=16.5
16.5+5.5=22
22+5.5=27.5
27.5+5.5=33
33+5.5=38.5
S17. Ans (e)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
390-10×9=300
300-8×7=244
244-6×5=214
214-4×3=202
202-2×1=200
S18. Ans (a)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
38+7=45
45-9=36
36+7=43
43-9=34
34+7=41
S19. Ans (d)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
7 25 45 69 99 137
+18 +20 +24 +30 +38
+2 +4 +6 +8
S20. Ans (e)
Sol.
The pattern of the series–
761-132=592
592-122=448
448-112=327
327-102=227
227-92=146
S21. Ans.(e)
Sol.
S22. Ans.(b)
Sol.
S23. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Pattern of series –
S24. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Pattern of series –
S25. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Pattern of series –
S26. Ans.(c)
Sol.
S27. Ans.(b)
Sol.
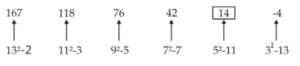
S28. Ans.(a)
Sol.
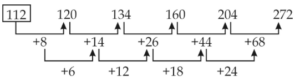
S29. Ans.(a)
Sol.
Pattern is —
+(11³+1), +(9³+1), +(7³+1), +(5³+1), +(33+1),
So, 5 + (11³ + 1) = 1337
S30. Ans.(c)
Sol.
Pattern is—
÷7, ×6, ÷5, ×4, ÷3, …
So, 427 ÷ 7 = 61
S31. Ans (b)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
404-16=388
388-24=364
364-32=332
332-40=292
292-48=244
244-56=188
So, Wrong number is 366.
S32. Ans (d)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
511÷2-0.5=255
255÷2-0.5=127
127÷2-0.5=63
63÷2-0.5=31
31÷2-0.5=15
15÷2-0.5=7
So, Wrong number is 512.
S33. Ans (e)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
520 563 613 670 734 805 883
+43 +50 +57 +64 +71 +78
+7 +7 +7 +7 +7
So, Wrong number is 521.
S34. Ans (a)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
137+3×4=149
149+5×6=179
179+7×8=235
235+9×10=325
325+11×12=457
457+13×14=639
So, Wrong number is 630.
S35. Ans (e)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
310+22=314
314+42=330
330+62=366
366+82=430
430+102=530
530+122=674
So, Wrong number is 312.
S36. Ans (c)
Pattern of series-
0.5×7=3.5
3.5×6=21
21×5=105
105×4=420
420×3=1260
1260×2=2520
So, Wrong number is 2500.
S37. Ans (a)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
2249-32=2240
2240-52=2215
2215-72=2166
2166-92=2085
2085-112=1964
1964-132=1795
So, Wrong number is 1796.
S38. Ans (d)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
18.5×2-2=35
35×2-4=66
66×2-6=126
126×2-8=244
244×2-10=478
478×2-12=944
So, Wrong number is 17.
S39. Ans (b)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
114 154 202 258 322 394 474
+40 +48 +56 +64 +72 +80
+8 +8 +8 +8 +8
So, Wrong number is 478.
S40. Ans. (e)
Sol.
598 611 628 647 670 699 730
+13 +17 +19 +23 +29 +31
So, Wrong number is 596.
S41. Ans (a)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
133+33=160
160+42=176
176+53=301
301+62=337
337+73=680
680+82=744
So, Wrong number is 130.
S42. Ans (b)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
711+(11×1)=722
722+(11×2)=744
744+(11×3)=777
777+(11×4)=821
821+(11×5)=876
876+(11×6)=942
So, Wrong number is 940.
S43. Ans (c)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
3×1+1=4
4×2+1=9
9×3+1=28
28×4+1=113
113×5+1=566
566×6+1=3397
So, Wrong number is 3396.
S44. Ans (d)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
445+22-1=448
448+33-1=474
474+42-1=489
489+53-1=613
613+62-1=648
648+73-1=990
So, Wrong number is 444.
S45. Ans (a)
Sol.
Pattern of series-
52=25
73=343
92=81
113=1331
132=169
153=3375
172=289
So, Wrong number is 125.
| Solutions | |||||||||
| 01 | a | 02 | a | 03 | d | 04 | e | 05 | b |
| 06 | d | 07 | b | 08 | a | 09 | e | 10 | e |
| 11 | a | 12 | b | 13 | c | 14 | d | 15 | c |
| 16 | e | 17 | e | 18 | a | 19 | d | 20 | e |
| 21 | e | 22 | b | 23 | c | 24 | c | 25 | a |
| 26 | c | 27 | b | 28 | a | 29 | a | 30 | c |
| 31 | b | 32 | d | 33 | e | 34 | a | 35 | e |
| 36 | c | 37 | a | 38 | d | 39 | b | 40 | e |
| 41 | a | 42 | b | 43 | c | 44 | d | 45 | a |




 Number Series Questions for SBI PO Exam
Number Series Questions for SBI PO Exam
 Simplification Questions for SBI PO Exam
Simplification Questions for SBI PO Exam
 Simplification Questions for SBI Clerk 2...
Simplification Questions for SBI Clerk 2...




