Q1.Volume of sphere and cylinder are equal and the radius of both is same. Find volume of cone whose base radius and height is same as that of cylinder?(Given height of cylinder is 16cm)
(a) 768π cm3
(b) 756π cm3
(c) 748π cm3
(d) 786π cm3
(e) 762π cm3
Q2. A circular tent is cylindrical to a height of 3 metres and conical above it. If its diameter is 105 m and the slant height of the conical portion is 53 m, calculate the length of the canvas 5 m wide to make the required tent.
(a) 3894
(b) 973.5
(c) 1947 m
(d) 1800 m
(e) None of these
Q3. A right circular cone is exactly fitted inside a cube in such a way that the edges of the base of the cone are touching the edges of one of the faces of the cube and the vertex is on the opposite face of the cube. If the volume of the cube is 125 cc, what is the approximate volume of the cone?
(a) 30 cc
(b) 27 cc
(c) 33 cc
(d) 44 cc
(e) 49 cc
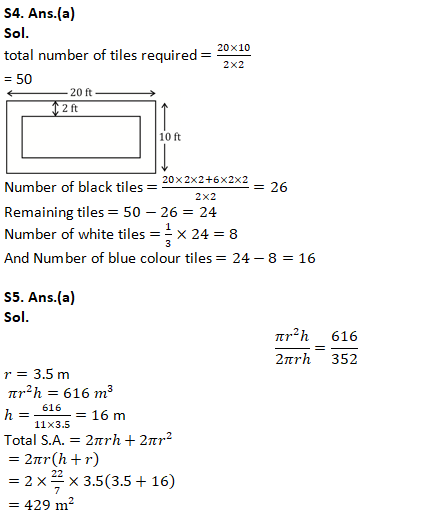
Q4. The length and the breadth of the floor of a room is 20 ft and 10 ft respectively. Square tiles of 2 ft dimension having three different colours are placed on the floor. The first row of tiles on all sides is of black colour, out of the remaining one-third is of white colour and the remaining are of blue colour. How many blue-colour tiles are there?
(a) 16
(b) 32
(c) 48
(d) 24
(e) 18
Q5. If the volume and curved surface area of a cylinder is 616 m^3and 352m2 respectively, what is the total surface area of the cylinder (in m^2)?
(a) 429
(b) 419
(c) 435
(d) 421
(e) 417
Directions (6-10): In the given questions, two quantities are given, one as ‘Quantity I’ and another as ‘Quantity II’. You have to determine relationship between two quantities and choose the appropriate option
Q6. The length of a passenger train moving at a speed of 45km/h is 250m. The length of a Rajdhani train is 750m which can move at a maximum speed of 135km/h.
Quantity I: Time taken by the passenger train to cross a person standing on the platform.
Quantity II: Time taken by the passenger train to cross the Rajdhani train coming from opposite direction.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q7. There are 3 vessels A, B and C full of mixture of milk and water. Vessel A contains 5 liters of water and 25 liters of milk, Vessel B contains 15 liters of water and 30 liters of milk and Vessel C contains water and milk in the ratio 1 : 5. 20%, 40% and 30% of the total mixtures from vessels A, B and C respectively is taken and poured into a fourth vessel. The ratio of milk and water in the fourth vessel is 16 : 5
Quantity I: Capacity of vessel C in litres.
Quantity II: 80 litres.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q8. P, Q and R can complete a piece of work in 8, 12 and 24 days respectively. They work on alternate days.
Quantity I: Time taken by them to complete the work if P works on day 1, Q works on day 2 and R works on day 3 and so on.
Quantity II: Time taken by them to complete the work if Q works on day 1, R works on day 2 and P works on day 3 and so on.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q9.
Quantity I→Sudhir invested Rs. 16000 in a scheme which earned him simple interest @ 15% per annum. After two years he withdrew the principal amount plus interest and invested the entire amount in another scheme for two years, which earned him compound interest @ 12% per annum. Total interest earned by Sudhir at the end of 4 years.
Quantity II → Sumit lent some money to Mohit at 5% per annum simple interest. Mohit lent the entire amount to Birju on the same day at 8 1/2% per annum. In this transaction after a year Mohit earned a profit of Rs. 350. Find the sum of money lent by Sumit to Mohit.
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I < Quantity II
(c) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(d) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
(e) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
Q10. Quantity I: Profit share of ‘A’.
A, B and C enter into a partnership. ‘A’ invests Rs. 4000 for the whole year, ‘B’ puts in Rs. 6000 at the first and increasing to Rs. 8000 at the end of 4 months, whilst C puts in at first Rs. 8000 but withdraw Rs. 2000 at the end of 9 months. Total annual profit is Rs. 56,500.
Quantity II: Amount which when lend on C.I. at 20% interest being compounded annually for 3 years, gives total interest equal to Rs.9100
(a) Quantity I > Quantity II
(b) Quantity I ≥ Quantity II
(c) Quantity I < Quantity II
(d) Quantity I = Quantity II or No relation
(e) Quantity I ≤ Quantity II
Directions (11-15): In each of these questions, two equations (I) and (II) are given. You have to solve both the equations and give answer
Q11.
(i) 4x² + 14x – 18 = 0
(ii) y² + 12y + 35 = 0
(a) if x>y
(b) if x≥y
(c) if x<y
(d) if x ≤y
(e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y.
Q12.
(i) 4x² + 17x – 42 = 0
(ii) y² + 21y + 90 = 0
(a) if x>y
(b) if x≥y
(c) if x<y
(d) if x ≤y
(e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y.
Q13.
(i) x² – 24x + 128 = 0
(ii) y² – 34y + 288 = 0
(a) if x>y
(b) if x≥y
(c) if x<y
(d) if x ≤y
(e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y.
Q14.
(i) 8x² – 30x + 28 = 0
(ii) 5y² – 8y + 3 = 0
(a) if x>y
(b) if x≥y
(c) if x<y
(d) if x ≤y
(e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y.
Q15.
(i) x² – 31x + 184 = 0
(ii) y² – 47x + 552 = 0
(a) if x>y
(b) if x≥y
(c) if x<y
(d) if x ≤y
(e) if x = y or no relation can be established between x and y.
Solution:

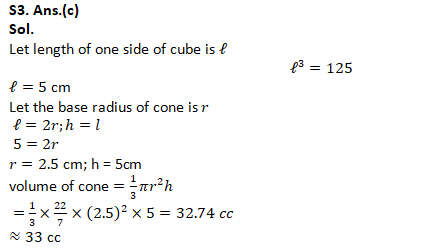



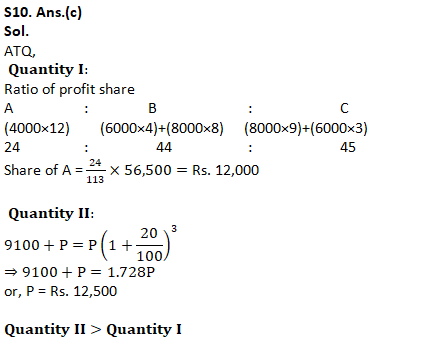
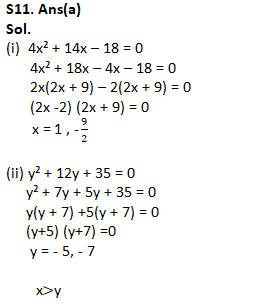
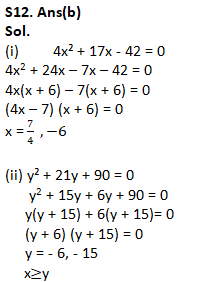
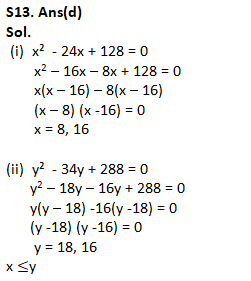
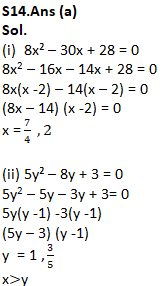
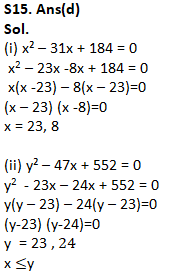



 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 ECGC PO Cut off 2025 Out, Check Final Cu...
ECGC PO Cut off 2025 Out, Check Final Cu...




