Q1. Disadvantages of linked list representation of binary trees over arrays?
(a) Randomly accessing is not possible
(b) Extra memory for a pointer is needed with every element in the list
(c) Difficulty in deletion
(d) Random access is not possible and extra memory with every element
(e) None of the above
Q2. Which of the following concepts means determining at runtime what method to invoke?
(a) Data Hiding
(b) Dynamic Typing
(c) Dynamic Binding
(d) Dynamic Loading
(e) Both (a) and (d)
Q3. Which of the following explains Cookies nature?
(a) Transient
(b) Volatile
(c) Intransient
(d) Non-Volatile
(e) Variable
Q4. Which is a unary operation?
(a) Selection operation
(b) Primitive operation
(c) Projection operation
(d) Generalized selection
(e) Both (a) and (b)
Q5. How to select all data from studentinfo table starting the name from letter ‘r’?
(a) SELECT * FROM studentinfo WHERE sname LIKE ‘r%’;
(b) SELECT * FROM studentinfo WHERE sname LIKE ‘%r%’;
(c) SELECT * FROM studentinfo WHERE sname LIKE ‘%r’;
(d) SELECT * FROM studentinfo WHERE sname LIKE ‘_r%’;
(e) SELECT & FROM studentinfo WHERE sname LIKE ‘+r’;
Q6. In SQL, the cross-tabs are created using:
(a) Slice
(b) Dice
(c) Pivot
(d) All of the mentioned
(e) None of the mentioned
Q7. In C++, which of the following belongs to the set of character types?
(a) char
(b) wchar_t
(c) only a
(d) Both wchar_t and char
(e) Both char and wchar
Q8. Which of the following statement(s) is TRUE?
(I) A hash function takes a message of arbitrary length and generates a fixed length code.
(II) A hash function takes a message of fixed length and generates a code of variable length.
(III) A hash function may give the same hash value for distinct messages.
(a) I only
(b) II and III only
(c) I and III only
(d) All I, II and III
(e) None of the above
Q9. In Chaining, what is the load factor?
(a) Average array size
(b) Average key size
(c) Average chain length
(d) New key size
(e) New array size
Q10. What is a hash table?
(a) A structure that maps values to keys
(b) A structure that maps keys to values
(c) A structure used for storage
(d) A structure used to implement stack and queue
(e) Both (c) and (d)




 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
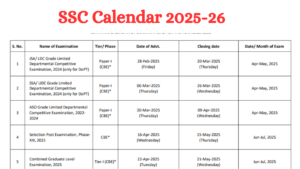 SSC Calendar 2025 Under Review, Dates So...
SSC Calendar 2025 Under Review, Dates So...





