Table of Contents
As the IBPS Specialist Officer (SO) Prelims 2024 exam concludes, aspirants eagerly await insights into the questions that were asked. Memory-based questions play a crucial role in helping candidates understand and analyse the exam’s difficulty level and understand the type of questions asked across various sections. This article provides an initial look at some of the questions from the exam, with a promise to update with the complete memory-based question set soon.
IBPS SO Prelims Memory Based 2024
The IBPS SO 2024 prelims exam tested candidates across three sections: English Language, Reasoning and Quantitative Aptitude/General Awareness. Candidates for various specialist roles, such as IT Officer, Agriculture Field Officer, HR/Personnel Officer and Marketing Officer, appeared in the exam. Based on initial feedback, the exam was moderately difficult, with questions designed to assess both conceptual knowledge and quick problem-solving abilities.
IBPS SO Prelims Memory Based 2024, Download PDF
The memory-based question set will provide a list of questions, covering all sections in greater detail. This full compilation will allow candidates to Analyze Sectional Weightage and Prepare for Future Exams.
IBPS SO Prelims Memory Based 2024: Download PDF (will be uploaded soon)
Below is a list of questions encountered in different sections. These questions are based on memory from candidates who appeared in the exam, offering a glimpse into the areas covered and the topics that were emphasized.
Directions (1-6): Read the following pie charts carefully and answer the questions given below. The pie chart I shows the percentage distribution of pastries baked by five bakeries. The pie chart II shows the percentage distribution of pastries sold by these five bakeries.
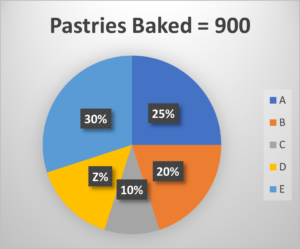
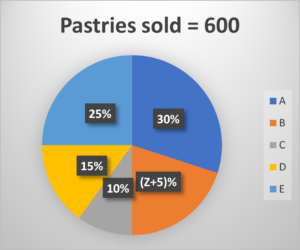
Q1. Find the ratio of the total number unsold pastries by B and E together to the total number of pastries baked by C.
(a) 1:2
(b) 2:1
(c) 3:1
(d) 1:4
(e) 4:3
Q2. Total number of pastries sold by A and B together is what percentage more or less than the total number of unsold pastries by A and D together?
(a) 133.67%
(b) 233.67%
(c) 33.33%
(d) 133.33%
(e) 233.33%
Q3. The total number of pastries sold by F is (Z+10)% more than that of B. If the number of unsold pastries by F and C is in the ratio of 8:5 respectively, then the total number of pastries baked by A is how much more or less than that of by F.
(a) 27
(b) 29
(c) 21
(d) 24
(e) 26
Q4. The ratio of puff to file pastries sold by D is 5:4 respectively. The number of puff pastries sold by E is 60% more than that of D. Find the difference between the number of filo pastries sold by D and E. (only two types of pastries sold by D and E)
(a) 20
(b) 24
(c) 30
(d) 45
(e) 48
Q5. If the price of each pastry sold by A, B, and D is Rs. Z, Z-3, and Z+5, respectively, then find the total revenue generated by A, B, and D to sell the pastries (in Rs).
(a) 5499
(b) 5490
(c) 5940
(d) 5540
(e) 5240
Q6. The average number of pastries baked by A, D, and E is what percentage of difference between the average number of pastries unsold and the average number of pastries sold by all the bakeries?
(a) 250%
(b) 275%
(c) 225%
(d) 350%
(e) 325%
Directions (7 – 10): In each of these questions a number series is given. In each series only one number is wrong. Find out the wrong number.
Q7. 179, 520, 1251, 2582, 4779, 8154, 13067
(a) 520
(b) 179
(c) 1251
(d) 2582
(e) 8154
Q8. 1504, 1248, 1052, 908, 808, 750, 708
(a) 808
(b) 1052
(c) 1248
(d) 1504
(e) 750
Q9. 10, 29, 55, 107, 211, 419, 825
(a) 10
(b) 29
(c) 55
(d) 825
(e) 419
Q10. 304, 319, 337, 359, 386, 419, 460
(a) 419
(b) 460
(c) 319
(d) 304
(e) 359
Directions (11-15): Study the following information carefully and answer the questions given below.
Nine persons – A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I – are seated in a single row facing north. Each person likes a different fruit- Apple, Mango, Plum, Cherry, Pear, Grapes, Orange, Kiwi and Guava. All the information provided is not necessarily in the given order.
B sits sixth to the right of the person who likes Plum. Three persons sit between the one who likes Plum and F. F sits immediate right of the person who likes Apple. The one who likes Cherry sits fourth to the left of the person who likes Apple. The person who likes Guava sits exactly between the person who likes Cherry and H. The person who likes Guava sits immediate right of person who likes Kiwi. One person sits between the person who likes Kiwi and G who doesn’t like Apple. As many persons sit to the right of G as to the left of the person who likes Strawberry. The one who likes Strawberry is an immediate neighbour of the person who likes Pear. Two persons sit between the person who likes Pear and E. The person who sits immediate right of E likes Grapes. More than three persons sit between the person who likes Grapes and Mango. C sits second to the right of the person who likes Mango and exactly between D and A. I and D are not immediate neighbours.
Q11. Who among the following sits immediate left of the one who sits fourth to the right of the person who likes Kiwi?
(a) The person who likes Pear
(b) The person who likes Grapes
(c) The person who likes Guava
(d) The person who likes Strawberry
(e) None of these
Q12. Which among the following combinations is/are correct?
(a) F – Mango
(b) H – Apple
(c) C – Cherry
(d) I – Kiwi
(e) None of these
Q13. What is the position of the person who likes Pear with respect to I?
(a) Fourth to the right
(b) Immediate left
(c) Fifth to the right
(d) Third to the left
(e) Fifth to the left
Q14. Four of the following five are alike in a certain way and form a group. Who among the following does not belong to the group?
(a) The one who likes Plum
(b) G
(c) The one who likes Apple
(d) B
(e) The one who likes Strawberry
Q15. How many persons sit between the person who likes Strawberry and D?
(a) Five
(b) Four
(c) Six
(d) Eight
(e) Three
Q16. How many pair of letters are in the word ‘BEAUTIFY’, each of which have as many letters between them as in the English alphabet (both forward and backward direction).
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) One
(e) More than four
Directions (17-20): In each question below, some statements are given following by five conclusions as five options. You have to take the given statements to be true even if they seem to be at variance with commonly known facts. Read the statements carefully and decide which of the conclusion definitely follows from the given statement, disregarding commonly known facts.
Q17. Statement:
Only a few March is July.
Only July is June.
Only a few April is July.
Conclusions:
(a) All March being July is a possibility.
(b) No April is March.
(c) No March being June is a possibility.
(d) All April being June is a possibility.
(e) Some July is not March.
Q18. Statement:
Only a few Yellow is Blue.
Only a few Red is Green.
All Blue is Red.
Conclusions:
(a) Some Yellow is not Red.
(b) No Blue is Green.
(c) All Yellow is Red.
(d) Some Blue is not Green is a possibility.
(e) No Yellow is Green.
Q19. Statement:
Some Light is not White.
Only a few Light is Colour.
Only White is Prism.
Conclusions:
(a) Some Light is not Prism is a possibility.
(b) All Light being Color is a possibility.
(c) Some Prism is Light.
(d) All White is Light.
(e) All Prism is not colour.
Q20. Statement:
Only Box is Bottle.
Only a few Mobile is Box.
No Box is Device.
Conclusions:
(a) Some Device being Bottle is a possibility.
(b) Some Mobile is Bottle.
(c) Some Box is not Mobile.
(d) No Mobile is Device.
(e) All Bottle being Mobile is a possibility.
Directions (21-25): Rearrange the following sentences to form a coherent paragraph.
(A) In recent years, the rapid advancements in technology have transformed how we communicate, work, and even think.
(B) This shift has not only influenced individual lifestyles but also significantly impacted entire industries and economies.
(C) The accessibility and affordability of digital tools have enabled more people to work remotely, access information instantly, and connect globally.
(D) As technology continues to evolve, its influence on society will only grow, bringing both opportunities and challenges.
(E) One prominent example of this transformation is the rise of digital platforms, which allow individuals to collaborate and share knowledge across vast distances.
(F) However, alongside these advantages, there are concerns about privacy, mental health, and the potential loss of human jobs to automation.
Q21. Which of the following statements is the FIRST statement after rearrangement?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) E
Q22. Which of the following statement is the SECOND statement after rearrangement?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) E
Q23. Which of the following statement is the THIRD statement after rearrangement?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) E
Q24. Which of the following statement is the FOURTH statement after rearrangement?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) F
Q25. Which of the following statement is the LAST statement after rearrangement?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) F
(d) D
(e) E
Directions (26-28): In the following questions, a sentence is divided into few parts. One of the few parts may be grammatically incorrect. Identify the incorrect part.
Q26. (A) The detailed analysis of the study’s findings, / (B) which were published in several scientific journals, / (C) provide a clear understanding of the impact / (D) of climate change on coastal ecosystems.
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) No error
Q27. (A) Many experts believe that the main reason for the decline in literacy rates / (B) is the rapid development of digital platforms / (C) which encourages more visual content consumption / (D) over traditional reading habits among young people.
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) No error
Q28. (A) While the organization has implemented various measures / (B) to reduce its carbon footprint, / (C) there remains several departments / (D) that have yet to fully comply with the guidelines.
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
(e) No error
Directions (29-30): In each of the following questions one sentence has been given. Each sentence has two blanks. From the options given below the sentence, pick the pair of words that fits into both the blanks respectively to make the sentence contextually meaningful and mark the letter corresponding to it as your answer.
Q29. Projects will ______________multi-modal connectivity infrastructure, _____________seamless movement of people, goods, and services.
(a)include, facilitated
(b)feature, ensuring
(c)offers, assisting
(d)highlighting, promoting
(e)present, ensures
Q30. The Indian market _______________the global trend of a bullish sentiment, primarily ______________by the expectation of a US interest rate cut in September.
(a)countered, fuel
(b)parallel, sparking
(c)matching, propelled
(d)aligned, trigger
(e) mirrored, driven
Tips for Analyzing and Using Memory-Based Questions
- Identify Key Areas: Focus on recurring topics such as puzzles in reasoning, DI in quant, and comprehension in English, which are usually consistent in such exams.
- Practice Time Management: Use these memory-based questions to simulate exam conditions, timing yourself to improve speed and accuracy.
- Refine Weak Areas: Compare your performance across these questions to identify and strengthen areas that may require more attention.
| Related Posts | |
| IBPS SO Previous Year Papers | IBPS SO Salary |
| IBPS SO Cut Off |
IBPS SO Vacancy 2024 |
| IBPS AFO Syllabus |
IBPS SO Law Officer Syllabus |
| IBPS SO Marketing Officer Syllabus | |




 GA Questions Asked in AIC MT Exam 2025, ...
GA Questions Asked in AIC MT Exam 2025, ...
 SBI Clerk Mains Memory Based Paper 2025,...
SBI Clerk Mains Memory Based Paper 2025,...
 SBI PO Prelims Memory Based Paper 2025, ...
SBI PO Prelims Memory Based Paper 2025, ...




