Q1. Arun takes 4 more days than Rana to complete a work. Yash is 20% more efficient than Rana and takes 1 less day Rana takes. Find the number of days taken by all of them to complete twice this work together? 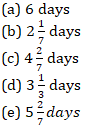

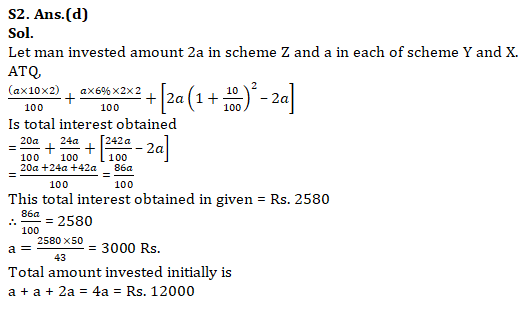
Q2. A man deposited his savings in 3 different schemes X, Y and Z and they offer SI at 10% per annum, SI at 6% per half year and CI at 10% per annum respectively. At the end of two years, total interest obtained by man from all the three schemes is Rs. 2580. Find initially total amount deposited by man, if amount invested in scheme Z is twice of each of scheme X and scheme Y and amount in both X and Y are same(in Rs.)?
(a) 3000
(b) 6000
(c) 9000
(d) 12000
(e) 6000
Q3. A shopkeeper have 3 juice machines, Ist for fresh oranges, then the remaining pulp(waste other than juice) of Ist machine is used in second and similarly remaining of 2nd machine is used for 3rd. If first machine, squeeze 90% by weight juice, second give 40% by weight and last give 16 ⅔% by weight juice. Find the amount of juice (in ml) obtained by shopkeeper in 1 kg of orange. [Assume 1 gm is equal to 1.05 ml]
(a) 950.5 ml
(b) 900 ml
(c) 1000 ml
(d) 950 m l
(e) 997.5 ml

Q4. A man bought two articles at different cost price and sold them, Ist at 12.5% profit and second at profit of 20%. The selling price of both the items is same and difference of profit earn on both is Rs. 10. Find the total cost price of both articles (in Rs.)?
(a) 280
(b) 300
(c) 310
(d) 320
(e) 350

Q5. Distance between Delhi and Jaipur is 300 km. Aman starts from Delhi and Rajiv from Jaipur at same time. After two hours, Aman realized he was travelling slow and therefore increased his speed by 25% and meet Rajiv at a point 108 km from Delhi. Find the increased speed of Aman, if Rajiv derived at a constant speed of 75 km/hr.
(a) 40 km/hr
(b) 50 km/hr
(c) 60 km/hr
(d) 55 km/hr
(e) 65 km/hr

Q6. A Cone cylinder and hemisphere have equal radius and height. Find the ratio of total surface area of cylinder, cone and hemisphere. 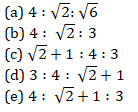
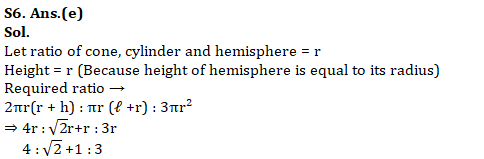
Q7. In how many ways word PERMUTATION written in which all vowels comes together?
(a) 19800
(b) 302400
(c) 78000
(d) 312400
(e) 4500
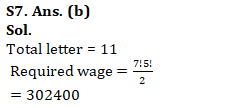
Q8. Difference between sum of 3 consecutive even numbers is 39 more than the sum of 3 consecutive odd number. If sum of smallest odd number and largest even number is 59 then find the sum of all six numbers.
(a) 175
(b) 170
(c) 167
(d) 177
(e) 155
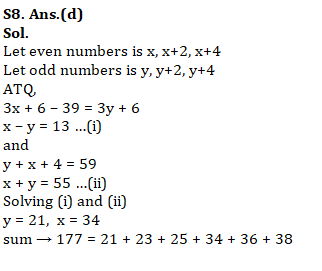
Q9. A container contained 80 kg of milk. From this container, 8 kg of mixture was taken out and replaced by water. This process was further repeated two times. How much milk is now contained by the container?
(a) 48 kg
(b) 56 kg
(c) 58.32 kg
(d) 59.46 kg
(e) None of these

Q10. A’s income is 25% more than B’s income, B’s income 10% less than C’s income and C’s income is 30% less than D’s income. If average income of all four is 15587.5 Rs. then find the income B.(in Rs)
(a) 12600
(b) 2000
(c) 14000
(d) 15250
(e) 18000
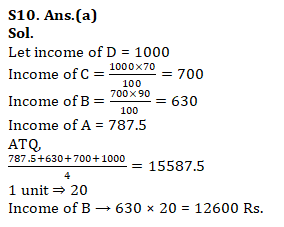
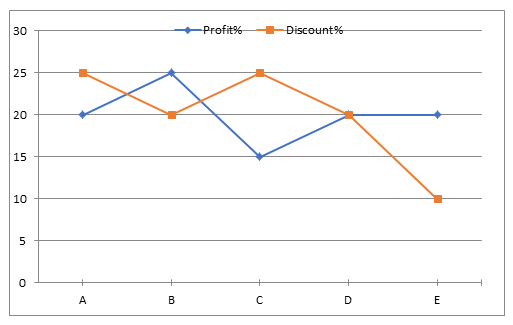
Directions (11-15): Line graph shows the profit % on CP of items (A, B, C, D& E) and discount% on MP of items.
Table shows number of items of each type shopkeeper have in IInd column and IIIrd column shows either MP or CP of item. Don’t assume unless it is mentioned in that question. MP, CP and SP stands for Marked price, cost price and selling price of item respectively.
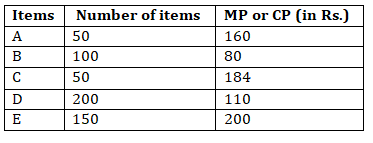
Q11. If MP of item A is shown and CP of item D is shown, then calculate the ratio of SP of item A to SP of item D.
(a) 9 : 11
(b) 11 : 7
(c) 7 : 11
(d) 10 : 11
(e) 11 : 8

Q12. If shopkeeper bought 50 items of C for Rs. 6000, and a person bought all of the items of C from him, then calculate the total amount of discount obtained by that person.
(a) 2300
(b) 46
(c) can’t be determined
(d) 900
(e) 3200

Q13. Let X be ratio of MP of 1 item to total SP of 2 items and Y be ratio of total MP of the 2 items to total CP of 3 items. Calculate Y : X of item E.
(a) 5 : 9
(b) 8 : 5
(c) can’t be determined
(d) 9 : 5
(e) 7 : 5
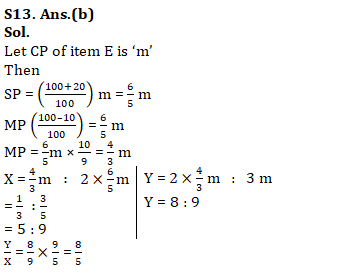
Q14. X is MP of item B when CP is given in table and Y is CP of item A when MP is given in table. Calculate X : Y.
(a) 4 : 5
(b) 8 : 5
(c) 6 : 1
(d) 5 : 8
(e) 5 : 4

Q15. Discount given on per item of B is Rs. 25. Calculate overall amount obtained if he sold all the items.
(a) 8000
(b) 12500
(c) 9500
(d) 10000
(e) can’t be determined

For 200+ most important arithmetic questions
- Quantitative Aptitude Study Notes for Bank Exams
- 100 MCQs Data Interpretation | Download Free PDF’s of DI
- Quantitative Aptitude Questions for all Competitive Exams
All the Best BA’ians for IBPS RRB PO/Clerk Main





 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 Without These Documents, Your Bank Exam ...
Without These Documents, Your Bank Exam ...





