Table of Contents
Theory of Demand- Economics is a subject that you have study for both the recruitment exams, SEBI Officer Grade A and UPSC EPFO Enforcement Officer recruitment exam. The NCERT is the benchmark when it comes to prepare the basics of Economics for competitive exLearn about the Demand Theory of Economics for UPSC EPFO Enforcement Officer and SEBI Grade A Officer Exams 2020.ams and here we have brought to you notes from Demand Theory of NCERT. You can also watch a YouTube Expert on Demand Theory given below for better understanding.
What is Demand?
Demand means effective desire or want for a commodity, which is backed by the ability and willingness to pay for it.
Goods: are physical, tangible objects used to satisfy people’s wants and needs.
Services: captures the intangible satisfaction of wants and needs.
Examples: Food items and clothes, are examples of goods, & Tasks that doctors and teachers perform for us as examples of services.
Also Check,
- UPSC EPFO Enforcement Officer Prime 2020 Online Test Series
- UPSC EPFO Complete Batch Enforcement Officer| Bilingual | Online Live Classes
- SEBI Grade A Phase-II | Bilingual | Live Classes
- SEBI Assistant Manager Phase I 2020 Online Test Series
Demand Function
The relation between the consumer’s optimal choice of the quantity of a good and its price is very important and this relation is called the demand function.
Thus, the consumer’s demand function for a good gives the amount of the good that the consumer chooses at different levels of its price when the other things remain unchanged.
It is Represented as q = d(p) where q denotes the quantity and p denotes the price of the good.
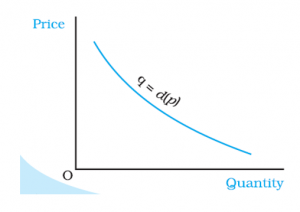
Law of Demand
Given the price of other goods, the consumer’s income and her tastes and preferences, the demand of a good is inversely related to the price of the good. Hence, the demand curve for a good is, in general, downward sloping. (Refer to the image above)
| SEBI Grade A 2020: Check Revised Exam Date | SEBI Grade A Paper-1 English Language Practice PDF | UPSC EPFO Previous Year Paper: Download Questions and Answer Key |
The inverse relationship between the consumer’s demand for a good and the price of the good is called the Law of Demand.
Law of Demand: If a consumer’s demand for a good moves in the same direction as the consumer’s income, the consumer’s demand for that good must be inversely related to the price of the good.
Demand Curve is a relation between the quantity of the good chosen by a consumer and the price of the good. The independent variable (price) is measured along the vertical axis and dependent variable (quantity) is measured along the horizontal axis. The demand curve gives the quantity demanded by the consumer at each price.
Exception to Law of Demand
Giffen goods are those goods whose demand is positively related to its Price. Giffen goods are named after Sir Robert Giffen.
What are Normal & Inferior Goods?
- The quantity of a good that the consumer demands can increase or decrease with the rise in income depending on the nature of the good. For most goods, demand increases as the consumer’s income increases and decreases as the consumer’s income decreases. Such goods are called normal goods.
- Those goods the demands for which move in the opposite direction of the income of the consumer. Such goods are called inferior goods.
- As the income of the consumer increases, the demand for an inferior good falls, and as the income decreases, the demand for an inferior good rises. Examples of inferior goods include low quality food items like coarse cereals.
What are Substitute Goods & Complementary Goods?
- The quantity of a good that the consumer chooses can increase or decrease with the rise in the price of a related good depending on whether the two goods are substitutes or complementary to each other.
- Goods which are consumed together are called complementary goods.
- Goods like tea and coffee are not consumed together. In fact, they are substitutes for each other.
Preparing for UPSC EPFO 2020? Fill the form to get all Study Material
| UPSC EPFO Salary, Job Profile and Promotion | For UPSC EPFO Study Material: Click Here | SEBI Grade A Officer Vs. RBI Grade B Officer |
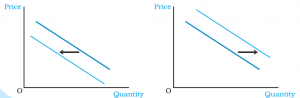
Shifts in the Demand Curve?
1. Changes in the Income of the consumer.
2. Change in the tastes and preferences
3. Price of substitutes has risen.
4. Price of complementary goods has declined.
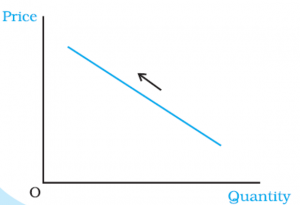
Movements along the Demand Curve
At higher prices, the demand is less, and at lower prices, the demand is more.
Thus, any change in the price leads to movements along the demand curve.
In case of any doubts, do mail us at blogger@adda247.com
Register to Get Study Materials SEBI Assistant Manager Recruitment 2020
| SEBI Grade A 2020: Check Revised Exam Date | SEBI Grade A Paper-1 English Language Practice PDF | UPSC EPFO Previous Year Paper: Download Questions and Answer Key |



 IBPS Final Result 2025 Coming Out Tomorr...
IBPS Final Result 2025 Coming Out Tomorr...
 Simple Tips to Avoid Common Mistakes In ...
Simple Tips to Avoid Common Mistakes In ...
 Important Topics & Shortcuts for IDB...
Important Topics & Shortcuts for IDB...


