Q1. The aim of drying is to____________
(a) Increase the moisture content
(b) Decrease the moisture content
(c) Both of a and b
(d) None the above
Q2. For effective natural drying method, the relative humidity of the air should be_____________
(a) More than 95%
(b) More than 90%
(c) More than 85%
(d) Less than 75%
Q3. ____________ is/ are the disadvantages of sun drying method.
(a) Slow drying process
(b) Depends on the weather
(c) High risk of contamination e Possible loss due to birds and rodents
(d) All of the above
Q4. ______________is the widest spread practice in semi-humid and humid conditions where natural drying cannot be used.
(a) Natural drying
(b) Forced hot air drying
(c) Dehumidified air-drying
(d) None of the above
Q5. In case of _______________ unheated dehumidified air is circulated through the grain mass, until the moisture content of the grain is reduced to the desired level.
(a) Natural drying
(b) Forced hot air drying
(c) Dehumidified air-drying
(d) None of the above
Q6. Floor dyer are suitable for______________
(a) Small grains
(b) Large grains
(c) All types grain
(d) None of the above
Q7.bag dryer is suitable for_____________
(a) Small grains
(b) Large grains
(c) Either A or B
(d) None of the above
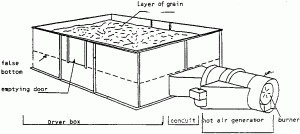
Q8. Box dryer is suitable for___________
(a) Tiny grains
(b) Large grains
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of the above
Q9. _________________ is suitable for quick and normal drying seeds, small to very small lots and chaffy seeds.
(a) Continuously flowing vertical dryers
(b) Continuously flowing belt dryers
(c) Rotary dryers
(d) None of the above
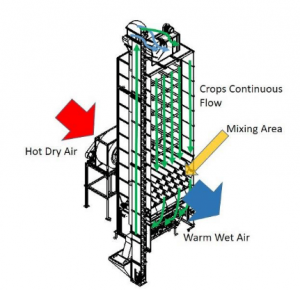
Q10. _________ is suitable for quick and normal drying and free flowing grains of single variety.
(a) Continuously flowing vertical dryers
(b) Continuously flowing belt dryers
(c) Rotary dryers
(d) None of the above
Solutions
S1. Ans(b)
Sol. The aim of drying is to lower the moisture content of the grain for safe storage and further processing.

S2. Ans(d)
Sol. for drying to be effective, the relative humidity of the ambient air must not be higher than 70%.
S3. Ans(d)
Sol. Disadvantages of sun drying method
• Slow drying process
• Depends on the weather
• High risk of contamination e Possible loss due to birds and rodents
• High labour input
S4. Ans(b)
Sol. Forced hot-air Drying: This is the widest spread practice in semi-humid and humid conditions where natural drying cannot be used. Artificially heated air is forced to flow through a mass of grain in bulk or in bags to absorb released moisture from grain mass.
S5. Ans(c)
Sol. Dehumidified air-drying: In case of dehumidified air-drying, unheated dehumidified air is circulated through the grain mass, until the moisture content of the grain is reduced to the desired level. It is more commonly applied when small quantities of grain must be dried to very low moisture content for being used as seed.

S6. Ans(c)
Sol. Floor dyers: Suitable for all grains of all sizes.

S7. Ans(b)
Sol. Bag dryers: Suitable for small grain lots to be used as seed where many varieties are handled (breeder and foundation seed).
S8. Ans(b)
Sol. Box dryers: Suitable for large grain lot where slow drying is required.
S9. Ans(b)
Sol. Continuously flowing belt dryers: Suitable for quick and normal drying seeds, small to very small lots and chaffy seeds.
S10. Ans(a)
Sol. Continuously flowing vertical dryers: Suitable for quick and normal drying and free flowing grains of single variety. Can handle large volume of grain. Not suitable for small lots of different varieties.



 GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
GA Capsule for SBI Clerk Mains 2025, Dow...
 The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
The Hindu Review October 2022: Download ...
 Important Days in April 2025, List of Na...
Important Days in April 2025, List of Na...




